Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters.
- Assessment Limits :
Units may be the same or different across the two quantities. - Calculator :
yes
- Context :
allowable
- Test Item #: Sample Item 1
- Question:
Nicole bought a meal in a town that has no sales tax. She tips 20%.
Select all meals Nicole could buy for less than or equal to $15.
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: MS: Multiselect
- Test Item #: Sample Item 2
- Question: James pays $120.00 for golf clubs that are on sale for 20% off at Golf Pros.
At Nine Iron, the same clubs cost $8.00 less than they cost at Golf Pros. They are on
sale for 13% off.
What is the original cost of the clubs at Nine Iron?
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: EE: Equation Editor
- Test Item #: Sample Item 3
- Question:
Ads Galore makes posters with standard dimensions of
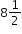 inches by 11 inches as shown.
inches by 11 inches as shown.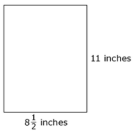
Both the length and width of the poster may vary by
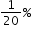 , according to Ads Galore's regulations.
, according to Ads Galore's regulations.What is the smallest acceptable area of one poster, rounded to the nearest thousandth of a square inch?
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: EE: Equation Editor
Related Courses
Related Access Points
Related Resources
Educational Games
Formative Assessments
Lesson Plans
Original Student Tutorials
Perspectives Video: Professional/Enthusiasts
Problem-Solving Tasks
Teaching Ideas
Tutorials
Unit/Lesson Sequence
Virtual Manipulative
STEM Lessons - Model Eliciting Activity
Students will explore and assess the implications various human and environmental factors are having on the yellow-legged frog population in California. Students will use knowledge of percentages to calculate population size and will complete research to explore the affects of human impact on the environment and the process of adaptation through natural and artificial selection.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx
Students will make decisions concerning features of their prom. Students will perform operations with percent and decimals to solve real-world problems involving money.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom.
Just how quickly is the world's human population growing? In the US and other developed countries, the current growth rate is slow compared to some developing countries where it is speeding up. There are factors that slowed down this growth rate and there are similar factors that actually speed it up. Discussing and explaining the factors that determine the fluctuation in growth rate.
The US population growth between 1950 - 2000 is 7.5 times slower than that of India. In 1950 the US had a population of 80 million which increased every ten years with 1 million.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom.
In this Model Eliciting Activity, MEA, students will work in cooperative groups to discuss and come up with a procedure to rank the banks from best to worst by estimating the simple interest and total loan amount.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom.
This Model Eliciting Activity (MEA) presents students with the real-world problem of contaminated drinking water. Students are asked to provide recommendations for a non-profit organization working to help a small Romanian village acquire clean drinking water. They will work to develop the best temporary strategies for water treatment, including engineering the best filtering solution using local materials. Students will utilize measures of center and variation to compare data, assess proportional relationships to make decisions, and perform unit conversions across different measurement systems.
The students will have to decide which van is the "best buy" for a family. They will have to figure monthly payments and will also use critical thinking skills to decide which is the best van to purchase.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom.
In this MEA, students will decide how many wolves to introduce into Yellowstone National Park's ecosystem. The number of wolves could influence many factors, from the tourism industry to local farming businesses, as well as the populations of other species in the area. Students must choose to introduce the number of wolves they feel will be most beneficial to the preservation of Yellowstone National Park as determined by the mission statement of Yellowstone and the National Park Service.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom.
MFAS Formative Assessments
Students are given gasoline prices from a year ago and today and are asked to calculate the percent change.
Students must find proportionally equivalent values given a set of rational number quantities.
Students are asked to calculate the amount of sales tax and total price, given prices of individual items to purchase.
Original Student Tutorials Mathematics - Grades 6-8
Follow Hailey and Kenna as they estimate tips and sales tax at the mall, restaurants, and the hair salon in this interactive tutorial.
Let's calculate markups and markdowns at the mall and follow Paige and Miriam working in this interactive tutorial.
Calculate simple interest and estimate monthly payments alongside a loan officer named Jordan in this interactive tutorial.
Explore sales tax, fees, and commission by following a customer service representative named Julian in this interactive tutorial.
Learn to solve percent change problems involving percent increases and decreases in in this interactive tutorial.
Roll up your sleeves and learn how proportions can be used in everyday life in this interactive tutorial.
Student Resources
Original Student Tutorials
Roll up your sleeves and learn how proportions can be used in everyday life in this interactive tutorial.
Type: Original Student Tutorial
Follow Hailey and Kenna as they estimate tips and sales tax at the mall, restaurants, and the hair salon in this interactive tutorial.
Type: Original Student Tutorial
Let's calculate markups and markdowns at the mall and follow Paige and Miriam working in this interactive tutorial.
Type: Original Student Tutorial
Calculate simple interest and estimate monthly payments alongside a loan officer named Jordan in this interactive tutorial.
Type: Original Student Tutorial
Explore sales tax, fees, and commission by following a customer service representative named Julian in this interactive tutorial.
Type: Original Student Tutorial
Learn to solve percent change problems involving percent increases and decreases in in this interactive tutorial.
Type: Original Student Tutorial
Educational Games
In this activity, students play a game of connect four, but to place a piece on the board they have to correctly estimate an addition, multiplication, or percentage problem. Students can adjust the difficulty of the problems as well as how close the estimate has to be to the actual result. This activity allows students to practice estimating addition, multiplication, and percentages of large numbers (100s). This activity includes supplemental materials, including background information about the topics covered, a description of how to use the application, and exploration questions for use with the java applet.
Type: Educational Game
In this activity, students are quizzed on their ability to estimate sums, products, and percentages. The student can adjust the difficulty of the problems and how close they have to be to the actual answer. This activity allows students to practice estimating addition, multiplication, or percentages of large numbers. This activity includes supplemental materials, including background information about the topics covered, a description of how to use the application, and exploration questions for use with the java applet.
Type: Educational Game
Perspectives Video: Professional/Enthusiast
<p>Ceramic glaze recipes are fluid and not set in stone, but can only be formulated consistently with a good understanding of math!</p>
Type: Perspectives Video: Professional/Enthusiast
Problem-Solving Tasks
The purpose of this task is to give students an opportunity to solve a challenging multistep percentage problem that can be approached in several different ways. Students are asked to find the cost of a meal before tax and tip when given the total cost of the meal. The task can illustrate multiple standards depending on the prior knowledge of the students and the approach used to solve the problem.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
In this task, students are presented with a real-world problem involving the price of an item on sale. To answer the question, students must represent the problem by defining a variable and related quantities, and then write and solve an equation.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Students are asked to determine how to distribute prize money among three classes based on the contribution of each class.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
The 7th graders at Sunview Middle School were helping to renovate a playground for the kindergartners at a nearby elementary school. City regulations require that the sand underneath the swings be at least 15 inches deep. The sand under both swing sets was only 12 inches deep when they started. The rectangular area under the small swing set measures 9 feet by 12 feet and required 40 bags of sand to increase the depth by 3 inches. How many bags of sand will the students need to cover the rectangular area under the large swing set if it is 1.5 times as long and 1.5 times as wide as the area under the small swing set?
Type: Problem-Solving Task
This problem includes a percent increase in one part with a percent decrease in the remaining and asks students to find the overall percent change. The problem may be solved using proportions or by reasoning through the computations or writing a set of equations.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Students are asked to make comparisons among the Egyptian, Gregorian, and Julian methods of measuring a year.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Students are asked to use proportional reasoning to answer a series of questions in the context of a recipe.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
The purpose of this task is to give students an opportunity to solve a multi-step ratio problem that can be approached in many ways. This can be done by making a table, which helps illustrate the pattern of taxi rates for different distances traveled and with a little persistence leads to a solution which uses arithmetic. It is also possible to calculate a unit rate (dollars per mile) and use this to find the distance directly without making a table.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
5,000 people visited a book fair in the first week. The number of visitors increased by 10% in the second week. How many people visited the book fair in the second week?
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Using the information provided find out how fast Anya rode her bike.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
This problem has multiple steps. In order to solve the problem it is necessary to compute: the value of the TunesTown shares; the total value of the BeatStreet offer of 20 million shares at $25 per share; the difference between these two amounts; and the cost per share of each of the extra 2 million shares MusicMind offers to equal to the difference.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Students are asked to determine which sale option results in the largest percent decrease in cost.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
The sales team at an electronics store sold 48 computers last month. The manager at the store wants to encourage the sales team to sell more computers and is going to give all the sales team members a bonus if the number of computers sold increases by 30% in the next month. How many computers must the sales team sell to receive the bonus? Explain your reasoning.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Students are asked to solve a problem using proportional reasoning in a real world context to determine the number of shares needed to complete a stock purchase.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Students are asked to solve a multistep ratio problem in a real-world context.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
After eating at your favorite restaurant, you know that the bill before tax is $52.60 and that the sales tax rate is 8%. You decide to leave a 20% tip for the waiter based on the pre-tax amount. How much should you leave for the waiter? How much will the total bill be, including tax and tip?
Type: Problem-Solving Task
The purpose of this task is for students to calculate the percent increase and relative cost in a real-world context. Inflation, one of the big ideas in economics, is the rise in price of goods and services over time. This is considered in relation to the amount of money you have.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
The purpose of this task is to see how well students students understand and reason with ratios.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Tutorials
This introductory video demonstrates the basic skill of how to write and solve a basic equation for a proportional relationship.
Type: Tutorial
This introductory video shows some basic examples of writing two ratios and setting them equal to each other. This is just step 1 when solving word problems with proportions.
Type: Tutorial
Learn how to find the full price when you know the discount price in this percent word problem.
Type: Tutorial
This site explicitly outlines the steps for using the proportion method to solve three different kinds of percent problems. It also includes sample problems for practice determining the part, the whole or the percent.
Type: Tutorial
Virtual Manipulative
In this online activity, students apply their understanding of proportional relationships by adding circles, either colored or not, to two different piles then combine the piles to produce a required percentage of colored circles. Students can play in four modes: exploration, unknown part, unknown whole, or unknown percent. This activity also includes supplemental materials in tabs above the applet, including background information about the topics covered, a description of how to use the application, and exploration questions for use with the Java applet.
Type: Virtual Manipulative
Parent Resources
Perspectives Video: Professional/Enthusiast
<p>Ceramic glaze recipes are fluid and not set in stone, but can only be formulated consistently with a good understanding of math!</p>
Type: Perspectives Video: Professional/Enthusiast
Problem-Solving Tasks
The purpose of this task is to give students an opportunity to solve a challenging multistep percentage problem that can be approached in several different ways. Students are asked to find the cost of a meal before tax and tip when given the total cost of the meal. The task can illustrate multiple standards depending on the prior knowledge of the students and the approach used to solve the problem.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
In this task, students are presented with a real-world problem involving the price of an item on sale. To answer the question, students must represent the problem by defining a variable and related quantities, and then write and solve an equation.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Students are asked to determine how to distribute prize money among three classes based on the contribution of each class.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
The 7th graders at Sunview Middle School were helping to renovate a playground for the kindergartners at a nearby elementary school. City regulations require that the sand underneath the swings be at least 15 inches deep. The sand under both swing sets was only 12 inches deep when they started. The rectangular area under the small swing set measures 9 feet by 12 feet and required 40 bags of sand to increase the depth by 3 inches. How many bags of sand will the students need to cover the rectangular area under the large swing set if it is 1.5 times as long and 1.5 times as wide as the area under the small swing set?
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Tom wants to buy some protein bars and magazines for a trip. He has decided to buy three times as many protein bars as magazines. Each protein bar costs $0.70 and each magazine costs $2.50. The sales tax rate on both types of items is 6½%. How many of each item can he buy if he has $20.00 to spend?
Type: Problem-Solving Task
This problem includes a percent increase in one part with a percent decrease in the remaining and asks students to find the overall percent change. The problem may be solved using proportions or by reasoning through the computations or writing a set of equations.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Students are asked to make comparisons among the Egyptian, Gregorian, and Julian methods of measuring a year.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Students are asked to use proportional reasoning to answer a series of questions in the context of a recipe.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
The purpose of this task is to give students an opportunity to solve a multi-step ratio problem that can be approached in many ways. This can be done by making a table, which helps illustrate the pattern of taxi rates for different distances traveled and with a little persistence leads to a solution which uses arithmetic. It is also possible to calculate a unit rate (dollars per mile) and use this to find the distance directly without making a table.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
5,000 people visited a book fair in the first week. The number of visitors increased by 10% in the second week. How many people visited the book fair in the second week?
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Using the information provided find out how fast Anya rode her bike.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
This problem has multiple steps. In order to solve the problem it is necessary to compute: the value of the TunesTown shares; the total value of the BeatStreet offer of 20 million shares at $25 per share; the difference between these two amounts; and the cost per share of each of the extra 2 million shares MusicMind offers to equal to the difference.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Students are asked to determine which sale option results in the largest percent decrease in cost.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
The sales team at an electronics store sold 48 computers last month. The manager at the store wants to encourage the sales team to sell more computers and is going to give all the sales team members a bonus if the number of computers sold increases by 30% in the next month. How many computers must the sales team sell to receive the bonus? Explain your reasoning.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Students are asked to solve a problem using proportional reasoning in a real world context to determine the number of shares needed to complete a stock purchase.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Students are asked to solve a multistep ratio problem in a real-world context.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
After eating at your favorite restaurant, you know that the bill before tax is $52.60 and that the sales tax rate is 8%. You decide to leave a 20% tip for the waiter based on the pre-tax amount. How much should you leave for the waiter? How much will the total bill be, including tax and tip?
Type: Problem-Solving Task
The purpose of this task is for students to calculate the percent increase and relative cost in a real-world context. Inflation, one of the big ideas in economics, is the rise in price of goods and services over time. This is considered in relation to the amount of money you have.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
The purpose of this task is to see how well students students understand and reason with ratios.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Teaching Idea
There are lots of ways to receive income, and lots of ways to spend it. In this EconomicsMinute teaching idea, students will develop two budgets, or plans, to help them decide how to allocate their income.
Type: Teaching Idea