Locate, order and compare numbers from 0 to 20 using the number line and terms less than, equal to or greater than.
Clarifications
Clarification 1: Within this benchmark, the expectation is not to use the relational symbols =,> or <.Clarification 2: When comparing numbers from 0 to 20, both numbers are plotted on the same number line.
Clarification 3: When locating numbers on the number line, the expectation includes filling in a missing number by counting from left to right on the number line.
General Information
Subject Area: Mathematics (B.E.S.T.)
Grade: K
Strand: Number Sense and Operations
Date Adopted or Revised: 08/20
Status: State Board Approved
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Equal Sign
- Number Line
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is to build on knowledge from comparing in MA.K.NSO.1.4 and to introduce the number line. This benchmark will deepen student understanding of the relationship between numbers, as well as provide the foundation for the number line as a strategy for operations later on.- Instruction includes varied orientations and ranges of the number line.
- For example, given number lines can be horizontal, vertical, starting at 0, starting at another number, include blanks or an open number line (MTR.5.1).
- Instruction includes making a connection to measurement when comparing numbers on a number line, which will help prepare students for using rulers in later grades.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students may assume that all number lines start at 0 or 1.
- When looking at number lines with hash marks, students may number the spaces between the hash marks instead of the hash marks.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
- Instruction includes building a number line using number cards. Students will benefit from experiences in which large number cards are used and placed on the floor so that students construct relationships about numbers and how far away or close they are to other numbers.
- Instruction focuses on building language for thinking about numbers and describing the location on the number line.
- For example, questions or statements that can be shared to elicit student thinking about numbers and their positions are:
- “Can you find the number 12?”
- “Where is 10? How far away is it to 12? How do you know?”
- “Is 11 greater than, or less than 13? How do you know?”
- “Here is the number 12. It comes before 13 and after 11.”
- “Ten is two away from 12.”
- “Eleven is less than 13 because it is two less than 13.”
- For example, questions or statements that can be shared to elicit student thinking about numbers and their positions are:
- Instruction includes building a number line to identify the value of hash marks.
- For example, using large number cards for the space and string/tape or marker to
represent the hash mark/value on the number line.
- Start at zero, place the number one next to the zero hash mark and then draw or identify the end of the card as the mark to represent one. Remove the large number card and replace with an arc/hop to show the jump from zero to one. Repeat this for each number up to 20.
- Scaffolds for building a number line can include providing the student with numbered strips to reference or using number cards to locate and match numbers on a number line.
- For example, using large number cards for the space and string/tape or marker to
represent the hash mark/value on the number line.
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1
In a small group, provide students with number lines and objects to count, like paperclips or bears. Ask students to represent two numbers, such as 7 and 9, using objects organized over the number line. Ask students which number is greater? How do they know? Allow students to share strategies and thinking with the group. Students should begin to understand that if there is more of one object, the count will extend further to the right.
Instructional Task 2
Provide students a number line to answer the questions below.- Part A. What’s the third number following 6?
- Part B. What’s the fifth number before 14?
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1
Find one more than 12 and one less than 12 on the number line. Show how you know.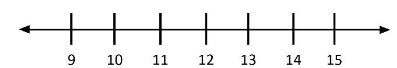
Instructional Item 2
Use a number line to show your thinking. Is 19 more than 17? Why or why not?
Instructional Item 3
What numbers are missing from the number line?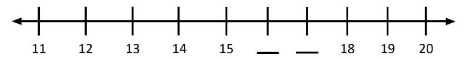
Related Courses
This benchmark is part of these courses.
5012020: Grade Kindergarten Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current))
7712015: Access Mathematics - Grade Kindergarten (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2018, 2018 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current))
5012005: Foundational Skills in Mathematics K-2 (Specifically in versions: 2019 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current))
Related Access Points
Alternate version of this benchmark for students with significant cognitive disabilities.
MA.K.NSO.2.AP.3: Locate and compare two numbers from 0 to 10 to determine which number is less than, equal to or greater than the other number.
Related Resources
Vetted resources educators can use to teach the concepts and skills in this benchmark.
Lesson Plans
Perspectives Video: Teaching Idea
Worksheets
Student Resources
Vetted resources students can use to learn the concepts and skills in this benchmark.
Worksheets
Parent Resources
Vetted resources caregivers can use to help students learn the concepts and skills in this benchmark.