Remarks
Example 1: Each unicycle made needs 1 wheel. Explain why w=u where w is the number of wheels and u is the number of unicycles describes this relationship.
Example 2: Each bicycle made needs 2 wheels. Explain why w=2b where w is the number of wheels and b is the number of bicycles describes this relationship.
Example 3: Each tricycle made needs 3 wheels. Explain why w=3t where w is the number of wheels and t is the number of tricycles describes this relationship.
Example 4: Below is a graph of the relationships in Examples 2 and 3. Explain why one of the lines is steeper than the other line.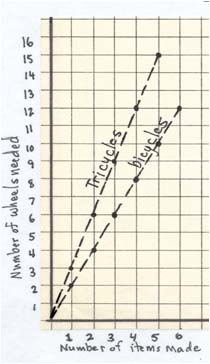
what would the graph of w=u look like?
-
Item Type(s):
This benchmark may be assessed using:
MC
item(s)
- Clarification :
Students will identify a table, graph, or equation that represents a linear function or other simple relationship.
Students will analyze a table or graph to identify or describe the rate of change.
Students will identify different representations of the same relationship, including translating among graphs, equations, tables, and words. - Content Limits :
Items may include tables, graphs, equations, or real-world situations.
Simple relationships may include discrete data that lends itself to a linear relationship.
Graphs should be limited to the first quadrant, and indicated points on the graphs must have whole-number coordinates.
Items will not include the use of the slope formula. - Stimulus Attributes :
Items should be set in a real-world or mathematical context.
- Test Item #: Sample Item 1
- Question: A cellular phone company charges a fixed monthly fee, plus $0.25 for each minute the phone is in use. The table shows that T, the total charge for one month, depends on m, the number of minutes the phone is in use.
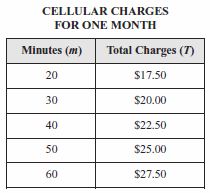
Which equation correctly shows the relationship between T and m?
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: MC: Multiple Choice
Related Access Points
Related Resources
Educational Software / Tool
Lesson Plans
Problem-Solving Task
Teaching Idea
Virtual Manipulative
Student Resources
Virtual Manipulative
This resource provides linear functions in standard form and asks the user to graph it using intercepts on an interactive graph below the problem. Immediate feedback is provided, and for incorrect responses, each step of the solution is thoroughly modeled.
Type: Virtual Manipulative






