Examples
A 60° angle is decomposed into two angles, one of which is 25°. What is the measure of the other angle?Clarifications
Clarification 1: Instruction includes the connection to angle measure as being additive.Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Angle
- Circle
- Right Angle
- Straight Angle
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is to extend student thinking about angle measures beyond right angles that were taught in grade 3 (MA.3.GR.1.1) and introducing the idea that angle measures are additive (MA.4.GR.1.2). Students will use this idea to find a missing angle measure.- For instruction, students should use protractors to draw angles that add up to make right angles, straight angles and circles.
- With the knowledge that angle measures are additive, students can solve interesting and challenging problems with all four operations to find the measurements of unknown angles on a diagram in real world and mathematical problems.
- Students can use a protractor to ensure that they develop understanding of benchmark angles (e.g., 30°, 45°, 60° and 90°).
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students may make errors when writing equations used to solve angle measurement problems. During instruction, expect students to justify their equations and solutions. Students may not understand that straight lines, even if intersected, measure 180°.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
- The teacher provides a right angle, straight angle, or circle and asks students to use the protractor to divide the angle into two angles and specify their measurements. The teacher has students write an equation to show that the sum of the two angles is equivalent to the angle they started with and explain their equation.
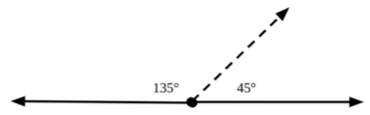
- For example, when provided with a straight angle, students divide the angle into a 45-degree angle and a 135-degree angle as show below. Students label each angle and explain the equation 135 + 45 = 180, knowing that a straight angle measures 180-degrees.
- Instruction includes matching equations with given angle images containing angle measures. Students explain the equations and how they know they match the image selected.
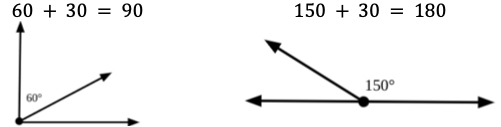
- For example, when provided images similar to those shown below, students match the equation from a list of equations provided and explain how they know the equation matches.
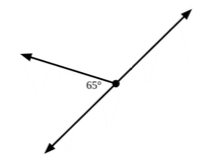
- The teacher provides images that contain missing angle measures. Students identify straight angles in the image and use their understanding that straight angles measure 180-degrees to help them find the missing angle measure.
- For example, when provided with the image below, students highlight or trace over the straight angle and label as 180-degrees. Students then write an equation using this information and the angle measure provided to help them solve for the unknown angle.
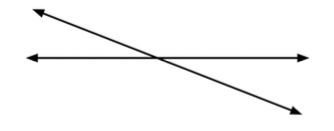
- Instruction includes identifying straight angles as measuring 180-degrees.
- For example, when provided images similar to the one shown below, students highlight straight angles and label them as 180-degrees. In this example, students identify both straight angles, highlighting them with different colors and explain that both have a measure of 180-degrees.
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1
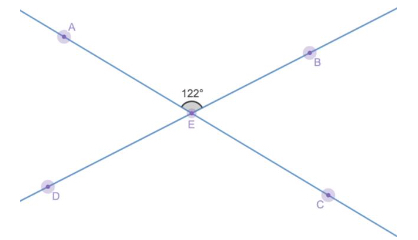
Two straight lines, AC and BD, intersect at point E. Using the given angle ∠AEB, find the measure of the other 3 angles.- This item may seem a bit challenging but it fits within the benchmark, because it can be solved by repeatedly using additivity, and that fact that a straight line is 180°.
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1
Carlos is adding angles together to create a 150° angle. Select all the angle measures that Carlos can use to create a 150° angle.- a. 50°+100°
- b. 45°+95°
- c. 50°+90°
- d. 50° +20° +20°
- e. 50° +50° +50°
*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.
Related Courses
Related Access Points
Related Resources
Formative Assessments
Lesson Plans
Original Student Tutorials
Perspectives Video: Teaching Ideas
Problem-Solving Task
MFAS Formative Assessments
Students are asked to determine an unknown angle measure that is one component of a larger known angle when given the other component.
Students are asked to recognize the additive nature of angles to determine an unknown angle measure.
Students are asked to determine adjacent angle measurements using the additive structure of angle measurement and known angle measurements.
Original Student Tutorials Mathematics - Grades K-5
Are you up for a challenge? You will use tile designs to explore how angles can be decomposed into smaller angles and how those parts can be shown as addends in equations in this interactive tutorial.
Note: this tutorial exceeds clarification limits and is meant as enrichment for students who met the standards to increase problem-solving skills.
Decompose and compose various angles while exploring clocks and windows in this interactive tutorial.
Note: this tutorial exceeds clarification limits and is meant as enrichment for students to improve their problem-solving skills.
Student Resources
Original Student Tutorials
Decompose and compose various angles while exploring clocks and windows in this interactive tutorial.
Note: this tutorial exceeds clarification limits and is meant as enrichment for students to improve their problem-solving skills.
Type: Original Student Tutorial
Are you up for a challenge? You will use tile designs to explore how angles can be decomposed into smaller angles and how those parts can be shown as addends in equations in this interactive tutorial.
Note: this tutorial exceeds clarification limits and is meant as enrichment for students who met the standards to increase problem-solving skills.
Type: Original Student Tutorial
Problem-Solving Task
The purpose of this task is to give students a problem involving an unknown quantity that has a clear visual representation. Students must understand that the four interior angles of a rectangle are all right angles and that right angles have a measure of 90° and that angle measure is additive.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Parent Resources
Problem-Solving Task
The purpose of this task is to give students a problem involving an unknown quantity that has a clear visual representation. Students must understand that the four interior angles of a rectangle are all right angles and that right angles have a measure of 90° and that angle measure is additive.
Type: Problem-Solving Task