Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters.
- Assessment Limits :
Circles are limited to whole circles and semicircles.
- Calculator :
Yes
- Context :
Allowable
- Test Item #: Sample Item 1
- Question:
A circle with its dimensions, in centimeters (cm), is shown.
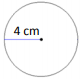
What is the area, in square centimeters, of the circle?
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: EE: Equation Editor
- Test Item #: Sample Item 2
- Question: A circle with its dimensions, in inches (in.), is shown.
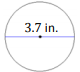
What is the area, in square inches, of half the circle?
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: EE: Equation Editor
- Test Item #: Sample Item 3
- Question: Mark placed a pool in his backyard, which is enclosed by a triangular fence.
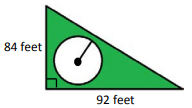
The radius of the pool is 20.5 feet. How much of the backyard area is not covered by the pool?
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: EE: Equation Editor
- Test Item #: Sample Item 4
- Question:
The circumference of a circle is 53.38 centimeters.
What is the area in square centimeters? Use 3.14 for
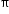
- Difficulty: N/A
- Type: EE: Equation Editor
Related Courses
Related Access Points
Related Resources
Formative Assessments
Lesson Plans
Original Student Tutorials
Perspectives Video: Professional/Enthusiasts
Perspectives Video: Teaching Ideas
Problem-Solving Tasks
Tutorials
Video/Audio/Animation
Virtual Manipulatives
STEM Lessons - Model Eliciting Activity
In this Model Eliciting Activities, MEA, students will calculate unit rate & circumference, compare & order decimals, convert metric units, and round decimals. Bubble Burst Corporation has developed some chewing gum prototypes and has requested the students to assist in the selection of which gum prototypes will be mass produced by using both quantitative and qualitative data to rank the prototypes for Bubble Burst Corporation.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought processes. MEAs follow a problem-based, student-centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEAs visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx
MFAS Formative Assessments
Students are asked to complete and explain an informal derivation of the relationship between the circumference and area of a circle.
Students are asked to write the formula for the area of a circle, explain what each symbol represents, and label the radius on a diagram.
Students are asked to write the formula for the circumference of a circle, explain what each symbol represents, and label the variables on a diagram.
Students are asked to solve a problem involving the circumference of a circle.
Original Student Tutorials Mathematics - Grades 6-8
Explore how to calculate the area of circles in terms of pi and with pi approximations in this interactive tutorial. You will also experience irregular area situations that require the use of the area of a circle formula.
Explore the origins of Pi as the ratio of Circumference to diameter of a circle. In this interactive tutorial you'll work with the circumference formula to determine the circumference of a circle and work backwards to determine the diameter and radius of a circle.
Learn to solve problems involving the circumference and area of circle-shaped pools in this interactive tutorial.
Student Resources
Original Student Tutorials
Explore the origins of Pi as the ratio of Circumference to diameter of a circle. In this interactive tutorial you'll work with the circumference formula to determine the circumference of a circle and work backwards to determine the diameter and radius of a circle.
Type: Original Student Tutorial
Explore how to calculate the area of circles in terms of pi and with pi approximations in this interactive tutorial. You will also experience irregular area situations that require the use of the area of a circle formula.
Type: Original Student Tutorial
Learn to solve problems involving the circumference and area of circle-shaped pools in this interactive tutorial.
Type: Original Student Tutorial
Problem-Solving Task
Students are asked to find the area of a shaded region using a diagram and the information provided. The purpose of this task is to strengthen student understanding of area.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Tutorials
This video shows how the area and circumference relate to each other and how changing the radius of a circle affects the area and circumference.
Type: Tutorial
In this video, students are shown the parts of a circle and how the radius, diameter, circumference and Pi relate to each other.
Type: Tutorial
This video shows how to find the circumference, the distance around a circle, given the area.
Type: Tutorial
In this video, watch as we find the area of a circle when given the diameter.
Type: Tutorial
Virtual Manipulative
This applet allows students to investigate the relationships between the area and circumference of a circle and its radius and diameter. There are three sections to the site: Intro, Investigation, and Problems.
- In the Intro section, students can manipulate the size of a circle and see how the radius, diameter, and circumference are affected. Students can also play movie clip to visually see how these measurements are related.
- The Investigation section allows students to collect data points by dragging the circle radius to various lengths, and record in a table the data for radius, diameter, circumference and area. Clicking on the x/y button allows students to examine the relationship between any two measures. Clicking on the graph button will take students to a graph of the data. They can plot any of the four measures on the x-axis against any of the four measures on the y-axis.
- The Problems section contains questions for students to solve and record their answers in the correct unit.
(NCTM's Illuminations)
Type: Virtual Manipulative
Parent Resources
Problem-Solving Task
Students are asked to find the area of a shaded region using a diagram and the information provided. The purpose of this task is to strengthen student understanding of area.
Type: Problem-Solving Task
Video/Audio/Animation
This video dynamically shows how Pi works, and how it is used.
Type: Video/Audio/Animation
Virtual Manipulative
This interactive lesson introduces students to the circle, its attributes, and the formulas for finding its circumference and its area. Students then perform a few calculations to practice finding the area and circumference of circles, given the diameter.
Type: Virtual Manipulative