Remarks
Students develop truth tables involving conjunctive, disjunctive, negation, conditional, and biconditional statements and use these truth tables to solve problems.
Example 1: What is the truth value of the following statement?
If the Earth is flat, then arsenic is healthy.
Example 2: Show that 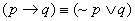 .
.
Example 3: Three students A, B, C owned a pet for some time and then disagreed as to who owns the animal. It is not certain that the responsibility of the ownership is desired. Each student makes one true and one false statement:
Student A claims
-It is C's pet
-I can make no claim to it
Student B claims
-C has no right to it
-It is A's pet
Student C claims
-It is my pet
-Student B's second statement is false.
Which student does the pet belong to?




