Find average and instantaneous rates of change. Explain the instantaneous rate of change as the limit of the average rate of change. Interpret a derivative as a rate of change in applications, including velocity, speed and acceleration.
Examples
Example: The vertical distance traveled by an object within the earth’s gravitational field, neglecting air resistance, is given by the equation x=0.5gt2 + vot + xo, where g is the force on the object due to earth's gravity, vo is the initial velocity, x0 is the initial height above the ground, t is the time in seconds and down is the negative vertical direction. Determine the instantaneous speed and the average speed for an object, initially at rest, 3 seconds after it is dropped from a 100 m. tall cliff. Describe the object 5 seconds after it is dropped from the same height. Use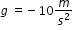 .
.
General Information
Subject Area: Mathematics (B.E.S.T.)
Grade: 912
Strand: Calculus
Standard: Apply derivatives to solve problems.
Date Adopted or Revised: 08/20
Status: State Board Approved
Related Courses
This benchmark is part of these courses.
1202300: Calculus Honors (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current))
Related Access Points
Alternate version of this benchmark for students with significant cognitive disabilities.
Related Resources
Vetted resources educators can use to teach the concepts and skills in this benchmark.
Perspectives Video: Expert
Student Resources
Vetted resources students can use to learn the concepts and skills in this benchmark.
Parent Resources
Vetted resources caregivers can use to help students learn the concepts and skills in this benchmark.