Examples
Example: One less than 40 is 39.Example: Ten more than 23 is 33.
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- NA
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is to bring a focus on place value and patterns that are found in numbers. In Kindergarten students counted forward and backward by 1s and 10s.- Instruction focuses on making the connection to the place value of digits.
- The expectation of the benchmark is not to focus on addition and subtraction strategies.
- Instruction includes use of a number line to reinforce the idea of one more, one less, and the use of a hundreds chart to focus students understanding about place value patterns.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Some students may confuse the place value when asked what is ten more or ten less and give a response that is only one more or one less. In these cases, using a hundreds chart may help students visually see what is ten more, ten less as well as one more, one less.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
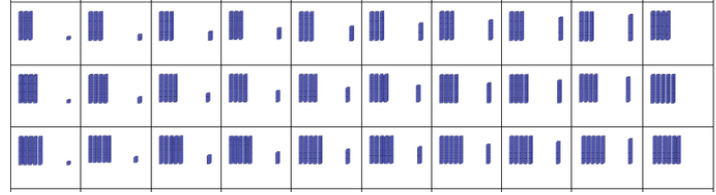
- Teacher provides a hundreds chart with the numbers identified with base ten blocks. Have students identify a specific number and ask them about the numbers that are 1 more, 1 less, 10 more, and 10 less.
- For example, the teacher asks students to identify the number 47. Once they identify the number on the chart ask, “Which number is one more than 47? [48] How do you know? Which number is 10 more than 47? [57] How do you know? How are they like 47? How are they different from 47? What is the relationship between the numbers and their place value?” Students provide other examples using any two-digit number they choose. (A portion of the chart is shown below.)
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.4.1, MTR.6.1)
What numbers should go in the blanks of the given equations below to make them true? Choose one statement and explain how you know you are correct.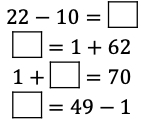
Instructional Task 2 (MTR.4.1, MTR.5.1)
Provide students with the chart below.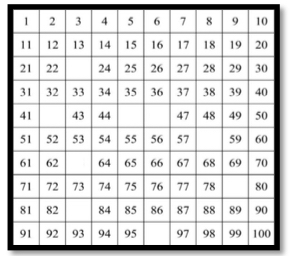
- Part A. Have students complete the chart independently.
- Part B. Facilitate a group discussion allowing students to explain the process or strategies
they used to complete the chart. Below are possible questions and student responses.
- How did you know that 23 was the missing number?
- Student responses may include: I know 23 is one more than 22. I know 23 is one less than 24. I know that 23 is 10 more than 13. I know that 23 is 10 less than 33.
- How many ways can you prove that 42 is the missing number between 41 and 43? What are those ways? Can you think of additional strategies to use?
- How did you know that 23 was the missing number?
Instructional Task 3 (MTR.7.1)
- Nevaeh has 33 blueberries. Jonathon has 10 more blueberries than Nevaeh. How many blueberries does Jonathon have?
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1
Complete the chart below to show one more, one less, ten more and ten less than 57.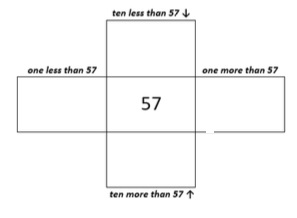
Instructional Item 2
What is one less than 98?*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.
Related Courses
Related Access Points
Related Resources
Formative Assessments
Lesson Plans
Original Student Tutorial
Worksheets
STEM Lessons - Model Eliciting Activity
Teams of students will use math to solve an open-ended, real-world problem to help their parent or caregiver choose the best babysitter. Students will apply mathematical skills of place value (two-digit number tens and ones) and counting to perform math calculations while analyzing data sets. This MEA will facilitate students demonstrating higher level critical thinking and problem solving during class discussions and in writing.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom.
MFAS Formative Assessments
Students solve a problem by mentally adding ten to a two-digit number.
Students solve a word problem by subtracting a multiple of 10 from a multiple of 10.
Original Student Tutorials Mathematics - Grades K-5
Explore strategies to add or subtract ten from a two-digit number in this interactive tutorial.
Student Resources
Original Student Tutorial
Explore strategies to add or subtract ten from a two-digit number in this interactive tutorial.
Type: Original Student Tutorial