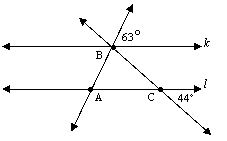General Information
Test Item Specifications
Students will determine the measures of angles in triangles and other polygons when some of the angle measures are given.
Polygons will not exceed a maximum of eight sides.
Graphics should be used in all of these items.
Items should be set in either a real-world or mathematical context.
Sample Test Items (2)
| Test Item # | Question | Difficulty | Type |
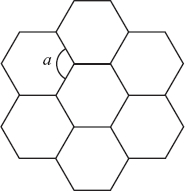
| Sample Item 1 | Lou is studying the design of a honeycomb. The honeycomb design is made up of regular hexagons, as shown below.
what is the measure, in degrees, of ∠ a above? |
N/A | MC: Multiple Choice |
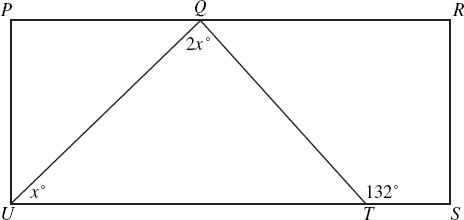
| Sample Item 2 | Vertices Q and T of ΔQTU are located on opposite sides of rectangle PRSU, as shown in the diagram below. what is the value of x? |
N/A | GR: Gridded-Response |
Related Resources
Image/Photograph
| Name | Description |
| Clipart: Geometric Shapes | In this lesson, you will find clip art and various illustrations of polygons, circles, ellipses, star polygons, and inscribed shapes. |
Lesson Plans
| Name | Description |
| The Ins and Outs of Polygons | In this lesson, students will explore how to find the sum of the measures of the angles of a triangle, then use this knowledge to find the sum of the measures of angles of other polygons. They will also be able to find the sum of the exterior angles of triangles and other polygons. Using both concepts, students will be able to find missing measurements. |
| How Many Degrees? | This lesson facilitates the discovery of a formula for the sum of the interior angles of a regular polygon. Students will draw all the diagonals from one vertex of various polygons to find how many triangles are formed. They will use this and their prior knowledge of triangles to figure out the sum of the interior angles. This will lead to the development of a formula for finding the sum of interior angles and the measure of one interior angle. |
Parent Resources
Image/Photograph
| Name | Description |
| Clipart: Geometric Shapes: | In this lesson, you will find clip art and various illustrations of polygons, circles, ellipses, star polygons, and inscribed shapes. |