General Information
Subject Area: X-Mathematics (former standards - 2008)
Grade: 8
Body of Knowledge: Algebra
Idea: Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
Big Idea: BIG IDEA 1 - Analyze and represent linear functions, and solve linear equations and systems of linear equations.
Date Adopted or Revised: 09/07
Content Complexity Rating:
Level 2: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts
-
More Information
Date of Last Rating: 06/07
Status: State Board Approved - Archived
Assessed: Yes
Test Item Specifications
Item Type(s):
This benchmark may be assessed using:
MC
item(s)
N/A
Clarification :
Students will identify an alternate representation of a function given in a rule, a table, a graph, or other symbolic representation.
Students will identify an alternate representation of a function given in a rule, a table, a graph, or other symbolic representation.
Content Limits :
Functions may include points from all four quadrants.
Values in equations should be rational numbers.
Items should present a table or graph and ask the student to identify another representation of the given function.
Functions may include points from all four quadrants.
Values in equations should be rational numbers.
Items should present a table or graph and ask the student to identify another representation of the given function.
Stimulus Attributes :
Items may be set in either a real-world or mathematical context.
Graphics should be used for all of these items.
Items may be set in either a real-world or mathematical context.
Graphics should be used for all of these items.
Sample Test Items (1)
| Test Item # | Question | Difficulty | Type |
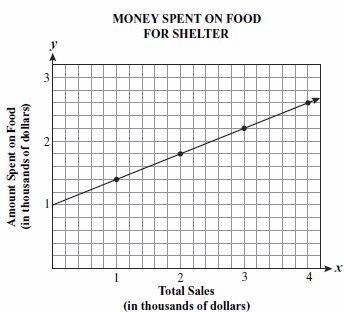
| Sample Item 1 | The graph below shows the linear relationship between the total sales at a thrift shop and the amount the thrift shop spent on food for a homeless shelter.
Which equation best represents the relationship shown in the graph? |
N/A | MC: Multiple Choice |
Related Resources
Lesson Plans
| Name | Description |
| Interpreting Distance-Time Graphs | This lesson takes a formative assessment approach to assessing whether students can interpret distance-time graphs. Whole-class discussion, group work, and individual activities help students interpret distance-time graphs related to real-world scenarios. |
| The Linear Function Connection | The students will compare two linear functions that have been represented in different ways (equation, table, graph, verbal description). They will be able to find and compare the rate of change, or slope, of the function from any of the representations. |
Problem-Solving Task
| Name | Description |
| Drip, Drop, Drip, Drop | Students design an experiment to model a leaky faucet and determine the amount of water wasted due to the leak. Using the data they gather in a table, students graph and write an equation for a line of best fit. Students then use their derived equation to make predictions about the amount of water that would be wasted from one leak over a long period of time or the amount wasted by several leaks during a specific time period. |
Tutorial
| Name | Description |
| Graphing Linear Functions | This is a video which explicitly demonstrates graphing linear functions using the x- and y-intercepts. |
Student Resources
Tutorial
| Name | Description |
| Graphing Linear Functions: | This is a video which explicitly demonstrates graphing linear functions using the x- and y-intercepts. |