General Information
Test Item Specifications
- Interpret a situation and represent the variables mathematically.
- Select appropriate mathematical methods.
- Interpret and evaluate the data generated.
- Communicate their reasoning clearly.
Students will solve problems involving surface area or volume of three-dimensional composite figures.
Students will solve problems involving surface area or volume using the decomposition of three-dimensional figures.
Three-dimensional figures used in composite figures are limited to three and may include right-rectangular prisms, right triangular prisms, right-square pyramids, right circular cylinders, and cones.
Problems related to surface area will not include cones, but problems related to volume can include cones.
Items that include cones and cylinders used in the composition or decomposition may include only whole figures, half-figures, or quarter-figures.
Right-square pyramids used in the composition or decomposition must be whole pyramids only.
Items will not include truncated cones and pyramids.
Dimensions of composite figures used in calculations will be whole numbers.
Graphics should be used in all of these items, as appropriate.
Items should be set in a real-world or mathematical context.
Sample Test Items (2)
| Test Item # | Question | Difficulty | Type |
| Sample Item 1 | Rebecca used a right circular cylinder piece of ice to cut out a cone. The dimensions of the ice piece she used are shown below.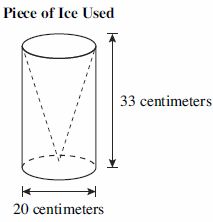 which is closest to the volume of the remaining ice after rebecca removes the largest cone possible from the right circular cylinder? |
N/A | MC: Multiple Choice |
| Sample Item 2 | A greenhouse has the shape of half a cylinder and a rectangular prism, as shown below.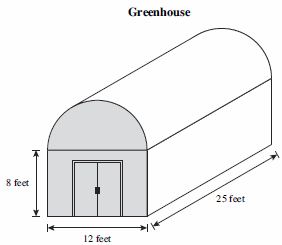 In order to air condition the building, the owner needs to know the volume of air space in the empty greenhouse. What is the volume, in cubic feet? |
N/A | GR: Gridded-Response |
Related Resources
Lesson Plan
| Name | Description |
| Cylinder Volume Lesson Plan | Using volume in the real world |
Teaching Idea
| Name | Description |
| Modeling: Making Matchsticks | This lesson unit is intended to help you assess how well students are able to:
|
Virtual Manipulative
| Name | Description |
| Surface Area of Prisms | This lesson is designed to develop students' knowledge of surface area and introduce them to calculating the surface area of a triangular prism. This lesson provides links to discussions and activities related to surface area as well as suggested ways to integrate them into the lesson. Finally, the lesson provides links to follow-up lessons designed for use in succession with the current one. |
