General Information
Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters.
Test Item Specifications
- translating between percents
- decimals and fractions
- representing percent increase and decrease as multiplication
- recognizing the relationship between increases and decreases
- starting temperature + change in temperature = final temperature
- final temperature – change in temperature = starting temperature
- final temperature – starting temperature = change in temperature
Complex fractions may be used, but should contain fractions with single-digit numerators and denominators
Neutral
Allowable
Sample Test Items (3)
| Test Item # | Question | Difficulty | Type |
| Sample Item 1 | At 8:00, the temperature was 6 degrees Celsius (°C). Three hours later, the
temperature was -13°C. By how many degrees Celsius did the temperature change? |
N/A | EE: Equation Editor |
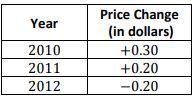
| Sample Item 2 | The change in the price of a certain brand of cereal from 2010 to 2012 is shown in
the table.
In 2009 the price of cereal was $3.69. What was the price of the cereal at the end of 2012? |
N/A | EE: Equation Editor |
| Sample Item 3 | The total change in the price of a certain brand of cereal from 2008 to 2012 was -$0.20. Complete the table to show possible price changes in 2010 and 2012.
|
N/A | TI: Table Item |
Related Courses
| Course Number1111 | Course Title222 |
| 1205020: | M/J Accelerated Mathematics Grade 6 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2020, 2020 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1205040: | M/J Grade 7 Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1204000: | M/J Foundational Skills in Mathematics 6-8 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 7812020: | Access M/J Grade 7 Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2018, 2018 - 2019, 2019 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
Related Resources
Formative Assessments
| Name | Description |
| Complex Fractions | Students are asked to rewrite complex fractions as simple fractions in lowest terms. |
| Positive and Negative Fractions | Students are asked to add, subtract, multiply, and divide positive and negative fractions. |
| Trail Mix Munchies | Students are asked to solve a word problem involving division of fractions. |
| A Rational Number Expression | Students are given a numerical expression to evaluate. |
| Monitoring Water Temperatures | Students are asked to solve a word problem that involves finding the average of positive and negative decimal numbers. |
Lesson Plans
| Name | Description |
| Budget Committee | In this MEA, students will take on the role as a member of the Sunshine County Budget Committee. Members will collaborate to determine the optimal sales tax rate, use that rate to calculate how much money can be used for special projects, then decide which special projects to include in the budget proposal. Students will use percentages to problem-solve in context while considering citizen input and constraints on spending. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Water, Water Everywhere - Natural Disaster Water Filtration | Students will be tasked with an engineering challenge to design an effective and efficient portable water filtration system. The designs will take dirty water and make it clear so it can be boiled for safe drinking. This lesson aligns to both math and science content standards. |
| Irrigation Station | This STEM lesson, complete with a design challenge, helps students design, build, and test irrigation methods. Students will incorporate and develop math skills through solving proportions as they work in teams to solve an engineering challenge. |
| NASA Salaries | This is a NASA-themed, MEA (Model Eliciting Activity) lesson that challenges students to solve a real world open ended problem, while promoting collaboration through teamwork. This lesson asks each group of students to choose five positions and assign salaries to the positions with a given budget of $500,000. The students' original decision (and "twist") will be based on information from the client's letter(s) and data set(s). Groups are to write a detailed letter to the client of the procedure used. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Laura’s Babysitting Job | In this 7th grade MEA Laura Banks requests a consulting firm, JJ Consulting, to help her make a decision on an employer. Students are to use the data table to calculate unit rates (nightly rate and hourly rate) and then rank her choices and write a recommendation with the procedure used to come up with the ranking. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Johansson Family Travel Plans | In this 7th grade MEA, students will form teams to rank the best vacation package for the Johansson family vacation. They will have to calculate the total cost of the vacation package making sure they don't go over budget. Teams will suggest what the family should do with any excess money. They will also suggest any deletion of activities if the package is over budget. Teams will make a presentation of the first choice recommendation. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Which van is the best buy? | The students will have to decide which van is the "best buy" for a family. They will have to figure monthly payments and will also use critical thinking skills to decide which is the best van to purchase. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Increasing and Decreasing Quantities by a Percent | This lesson unit is intended to help you assess how well students are able to interpret percent increase and decrease, and in particular, to identify and help students who have the following difficulties: |
| Best Chicken Franchise | In this MEA, the students will compare data to decide which franchise would be best for a person wanting to open their own fried chicken franchise. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought processes. MEAs follow a problem-based, student-centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEAs visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx. |
| Run For Your Life! | Based on a student-focused scenario encouraging healthier lifestyles, students will perform a close and careful reading of an article encouraging active and healthy lifestyles. During the lesson, students will analyze data from Consumer Reports comparing and contrasting treadmills and elliptical exercisers. Using information gathered, students will compile data and persuade administrators to buy equipment that will align with the provided budget and fit in the given space. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Using Positive and Negative Numbers in Context | This lesson unit is intended to help you assess how well students are able to understand and use directed numbers in context. It is intended to help identify and aid students who have difficulties in ordering, comparing, adding, and subtracting positive and negative integers. Particular attention is paid to the use of negative numbers on number lines to explore the following structures:
|
| Decisions, Decisions! | In this Model Eliciting Activity, MEA, students will research a list of companies to invest in through purchasing stocks. Students will calculate the amount invested and readjust their investment choices. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Pricing Twelve Days of Celebration | Students will discover how much items would cost if they were to give gifts for 12 days. They will learn how to calculate and add sales tax to find a total. |
| Batteries Included | In this Model Eliciting Activity, MEA, students will evaluate batteries using empirical data and customer comments to help a Taxi Cab Service decide which battery brand to purchase. In this real-world scenario, students will communicate with the client in letter format stating their suggested ranking. They will also provide calculations and justification for each decision. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought processes. MEAs follow a problem-based, student-centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Where in the world? | This resource provides a Model-Eliciting Activity where students will analyze a real-world scenario to solve a client's problem and provide the best possible solution based on a logically justified process. The students will consider a request from Always On Time Delivery Service to evaluate several GPS units and help them decide which unit they should purchase. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought processes. MEAs follow a problem-based, student-centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEAs visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Whirl Wind | The Whirl Wind Corporation would like to install Wind Turbines in the Mojave Desert. The company produces various models of these turbines and is looking for help in selecting the best one for the job. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Wallpaper Woes Money Math: Lessons for Life | Students hear a story about a middle-school student who wants to redecorate his bedroom. They measure the classroom wall dimensions, draw a scale model, and incorporate measurements for windows and doors to determine the area that could be covered by wallpaper. Students then hear more about the student's redecorating adventure and learn about expenses, budget constraints, and tradeoffs. |
Original Student Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| Order of Operations with Rational Numbers Part 2: Decimals | Evaluate numerical expressions with rational numbers expressed as decimals using the order of operations and properties of operations in this interactive tutorial. |
| Order of Operations with Rational Numbers Part 1: Fractions | Evaluate numerical expressions with rational numbers expressed as fractions using the order of operations and properties of operations in this interactive tutorial. This is part 1 in a two-part series. |
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name | Description |
| Sharing Prize Money | Students are asked to determine how to distribute prize money among three classes based on the contribution of each class. |
| Space Math: Lunar Cratering | Students explore the formation of craters on the lunar surface using real world imaging data and mathematical reasoning. Students make observations and inferences about the time that impact craters were formed using probability and percentages. |
Teaching Idea
| Name | Description |
| Feeding Time-SeaWorld Classroom Activity | Students determine the cost to feed a group of ocean animals in captivity, thus solving a real-life problem. |
Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| Multi-Step Word Problem | Solve a multi-step word problem in the context of a cab fare. |
| Rational Number Word Problem with Fractions | In this example, you determine the volume of frozen water and express the answer as a fraction. |
| Dividing Fractions Example 2 | This video demonstrates dividing fractions as multiplying by the reciprocal. |
| Dividing Whole Numbers and Fractions: T-shirts | This video demonstrates dividing a whole number by a fraction by multiplying by the reciprocal. |
| Interpreting absolute value as distance | In this video, we work through a bunch of examples that stretch our thinking on interpreting absolute value. |
| Examples of Evaluating Variable Expressions | This video tutorial shows examples of writing expressions in simplified form and evaluating expressions. |
Student Resources
Original Student Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| Order of Operations with Rational Numbers Part 2: Decimals: | Evaluate numerical expressions with rational numbers expressed as decimals using the order of operations and properties of operations in this interactive tutorial. |
| Order of Operations with Rational Numbers Part 1: Fractions: | Evaluate numerical expressions with rational numbers expressed as fractions using the order of operations and properties of operations in this interactive tutorial. This is part 1 in a two-part series. |
Problem-Solving Task
| Name | Description |
| Sharing Prize Money: | Students are asked to determine how to distribute prize money among three classes based on the contribution of each class. |
Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| Multi-Step Word Problem : | Solve a multi-step word problem in the context of a cab fare. |
| Rational Number Word Problem with Fractions: | In this example, you determine the volume of frozen water and express the answer as a fraction. |
| Dividing Fractions Example 2: | This video demonstrates dividing fractions as multiplying by the reciprocal. |
| Dividing Whole Numbers and Fractions: T-shirts: | This video demonstrates dividing a whole number by a fraction by multiplying by the reciprocal. |
| Examples of Evaluating Variable Expressions: | This video tutorial shows examples of writing expressions in simplified form and evaluating expressions. |
Parent Resources
Problem-Solving Task
| Name | Description |
| Sharing Prize Money: | Students are asked to determine how to distribute prize money among three classes based on the contribution of each class. |