General Information
Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters.
Test Item Specifications
Whole number bases.
Whole number exponents.
No
Allowable
Sample Test Items (3)
| Test Item # | Question | Difficulty | Type |
| Sample Item 1 | Which value is equivalent to the expression
|
N/A | MC: Multiple Choice |
| Sample Item 2 | Select all the expressions that are equivalent to
|
N/A | MS: Multiselect |
| Sample Item 3 | What is the value of |
N/A | EE: Equation Editor |
Related Courses
| Course Number1111 | Course Title222 |
| 1205010: | M/J Grade 6 Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1205020: | M/J Accelerated Mathematics Grade 6 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2020, 2020 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1204000: | M/J Foundational Skills in Mathematics 6-8 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 7812015: | Access M/J Grade 6 Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2018, 2018 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 7912110: | Fundamental Explorations in Mathematics 1 (Specifically in versions: 2013 - 2015, 2015 - 2017 (course terminated)) |
Related Resources
Formative Assessments
| Name | Description |
| Cube House | Students are asked to write a numerical expression using exponents. |
| Exponent Priorities | Students are asked to evaluate numerical expressions with exponents. |
| Paul’s Pennies | Students are asked to write and evaluate a numerical expression using exponents. |
| Evaluating Exponents | Students are asked to expand and evaluate exponential expressions containing whole number exponents. |
Lesson Plans
| Name | Description |
| Gather Data For Distribution by Programming an App | This lesson allow students to gather, calculate, and plot data using both computer code and mathematical equations. In this lesson students will create a pedometer app to demonstrate the understanding of algorithms, components (such as buttons, textboxes, sensors, etc.), and If/Then statements. This lesson uses algebraic equations and random data to access the needed components to store data in a spreadsheet. |
| Data Sets Represented in Computers | This lesson shows how data can be represented by computers, in relation to everyday activities we may not be aware that we use computer. It gives an overview of graphing data by creating a histogram based on population data. Using the data collected, students will get a chance to hand write code to show what structure is needed for computers to collect, analyze and distribute such data. This lesson is lesson 1 of the Data Set and Deviation Statistics Unit and bridges statistical concepts of data collection, graphing and analysis with programming a computer using coding language while reinforcing foundational algebraic skills. |
| Energy From The Sun To Make Some Fun! | MSP Racing Company is a cutting edge company that wishes to break through and develop the fastest renewable energy vehicle of its kind. In this lesson, students will be divided into teams of three and will be assigned the task of developing a solar-powered race car to be purchased and developed in full scale by MSP Racing. Each group of students will be employees of MSP Racing Company and will have to develop, test, and present their car to the boss (teacher) of the company. |
| The Power of Exponents | Students will be introduced to the power of exponents through the parable A Grain of Rice, by Demi. Students analyze the parts of an exponential expression and evaluate the expression using mental math and paper and pencil. |
| The "Power" of Exponents | The students will use square tiles or cubes to explore the meaning of "squared" and "cubed" numbers. They will model squared and cubed numbers to build a strong foundation for working with exponents. The students will learn the connections between area and volume models and the related positive exponents. This is an introductory lesson. |
| It's Hip 2b^2 eXponent^s | Meaning of Exponents... Students will write and simplify numerical and algebraic expressions with natural number exponents. Bases are limited to positive integers. |
Original Student Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| Order of Operations with Fractions | Evaluate numerical expressions with fractions using the order of operations and properties of operations in this interactive tutorial. |
| Order of Operations with Decimals | Evaluate numerical expressions with decimals using the order of operations and properties of operations in this interactive tutorial. |
| Order of Operations with Whole Numbers: Part 2 | Evaluate numerical expressions with whole numbers using the order of operations and properties of operations in this interactive tutorial. This is part 2 of a series on evaluating expressions with whole numbers. |
| Order of Operations with Integers | Evaluate numerical expressions with integers using the order of operations and properties of operations in this interactive tutorial. |
| MacCoder’s Farm Part 2: Condition Statements | Explore computer coding on the farm by using condition and IF statements in this interactive tutorial. You'll also get a chance to apply the order of operations as you using coding to solve problems. Click below to check out the other tutorials in the series. |
| MacCoder’s Farm Part 1: Declare Variables | Explore computer coding on the farm by declaring and initializing variables in this interactive tutorial. You'll also get a chance to practice your long division skills. |
| Order of Operations with Whole Numbers | Evaluate numerical expressions with whole numbers using the order of operations and properties of operations in this interactive tutorial. |
Problem-Solving Tasks
| Name | Description |
| The Djinni’s Offer | Students are asked to explore and then write an expression with an exponent. The purpose of this task is to introduce the idea of exponential growth and then connect that growth to expressions involving exponents. It illustrates well how fast exponential expressions grow. |
| Watch out for Parentheses | This problem asks the student to evaluate three numerical expressions that contain the same integers yet have differing results due to placement of parentheses. |
Student Center Activity
| Name | Description |
| Edcite: Mathematics Grade 6 | Students can practice answering mathematics questions on a variety of topics. With an account, students can save their work and send it to their teacher when complete. |
Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| Powers of Zero | Students will learn that non-zero numbers to the zero power equal one. They will also learn that zero to any positive exponent equals zero. |
| Patterns in Raising 1 and -1 to Different Powers | You will discover rules to help you determine the sign of an exponential expression with a base of -1. |
| Introduction to Order of Operations | Students will evaluate expressions using the order of operations. |
| Order of Operations | This video will show how to evaluate expressions with exponents using the order of operations.
|
| Introduction to Exponents | This video demonstrates how to evaluate expressions with whole number exponents. |
| The Zero Power | Learn why a number raised to the zero power equals 1. |
Unit/Lesson Sequence
| Name | Description |
| Using the Laws of Arithmetic | This lesson unit helps teachers assess how students perform arithmetic operations, write and evaluate numerical expression s from diagrammatic representations, apply the distributive and commutative properties, and find areas of compound rectangles. The time for the lesson is broken into a 15 minute pre-lesson task, an 80 minute lesson (or two 40 minute lessons), and a 15 minute follow up lesson or homework. Individual students will need a copy of the two tasks, a mini-whiteboard, a pen, and an eraser. Each small group will need cut-up copies of the card sets, a large sheet of poster-sized paper, and a glue stick. |
Virtual Manipulative
| Name | Description |
| Order of Operations Quiz | In this activity, students practice solving algebraic expressions using order of operations. The applet records their score so the student can track their progress. This activity allows students to practice applying the order of operations when solving problems. This activity includes supplemental materials, including background information about the topics covered, a description of how to use the application, and exploration questions for use with the java applet. |
Student Resources
Original Student Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| Order of Operations with Fractions: | Evaluate numerical expressions with fractions using the order of operations and properties of operations in this interactive tutorial. |
| Order of Operations with Decimals: | Evaluate numerical expressions with decimals using the order of operations and properties of operations in this interactive tutorial. |
| Order of Operations with Whole Numbers: Part 2: | Evaluate numerical expressions with whole numbers using the order of operations and properties of operations in this interactive tutorial. This is part 2 of a series on evaluating expressions with whole numbers. |
| Order of Operations with Integers: | Evaluate numerical expressions with integers using the order of operations and properties of operations in this interactive tutorial. |
| MacCoder’s Farm Part 2: Condition Statements: | Explore computer coding on the farm by using condition and IF statements in this interactive tutorial. You'll also get a chance to apply the order of operations as you using coding to solve problems. Click below to check out the other tutorials in the series. |
| MacCoder’s Farm Part 1: Declare Variables: | Explore computer coding on the farm by declaring and initializing variables in this interactive tutorial. You'll also get a chance to practice your long division skills. |
| Order of Operations with Whole Numbers: | Evaluate numerical expressions with whole numbers using the order of operations and properties of operations in this interactive tutorial. |
Problem-Solving Task
| Name | Description |
| The Djinni’s Offer: | Students are asked to explore and then write an expression with an exponent. The purpose of this task is to introduce the idea of exponential growth and then connect that growth to expressions involving exponents. It illustrates well how fast exponential expressions grow. |
Student Center Activity
| Name | Description |
| Edcite: Mathematics Grade 6: | Students can practice answering mathematics questions on a variety of topics. With an account, students can save their work and send it to their teacher when complete. |
Tutorials
| Name | Description |
| Powers of Zero: | Students will learn that non-zero numbers to the zero power equal one. They will also learn that zero to any positive exponent equals zero. |
| Patterns in Raising 1 and -1 to Different Powers: | You will discover rules to help you determine the sign of an exponential expression with a base of -1. |
| Introduction to Order of Operations: | Students will evaluate expressions using the order of operations. |
| Order of Operations : | This video will show how to evaluate expressions with exponents using the order of operations.
|
| Introduction to Exponents: | This video demonstrates how to evaluate expressions with whole number exponents. |
| The Zero Power: | Learn why a number raised to the zero power equals 1. |
Virtual Manipulative
| Name | Description |
| Order of Operations Quiz: | In this activity, students practice solving algebraic expressions using order of operations. The applet records their score so the student can track their progress. This activity allows students to practice applying the order of operations when solving problems. This activity includes supplemental materials, including background information about the topics covered, a description of how to use the application, and exploration questions for use with the java applet. |
Parent Resources
Problem-Solving Task
| Name | Description |
| The Djinni’s Offer: | Students are asked to explore and then write an expression with an exponent. The purpose of this task is to introduce the idea of exponential growth and then connect that growth to expressions involving exponents. It illustrates well how fast exponential expressions grow. |

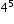 ?
?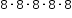 .
.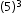 ?
?