General Information
Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters.
Test Item Specifications
Items may require a comparison of the values of digits across multiple place values, including whole numbers and decimals from millions to thousandths.
No
Allowable
Sample Test Items (4)
| Test Item # | Question | Difficulty | Type |
| Sample Item 1 | What is the missing value in the equation shown?
|
N/A | EE: Equation Editor |
| Sample Item 2 | What is the value of the missing number in the following equation?
|
N/A | MC: Multiple Choice |
| Sample Item 3 | How many times the value of 0.034 is the value of 0.34? |
N/A | EE: Equation Editor |
| Sample Item 4 | Which statements about the values 0.034 and 3.40 are true?
|
N/A | MS: Multiselect |
Related Courses
| Course Number1111 | Course Title222 |
| 5012070: | Grade Five Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 7712060: | Access Mathematics Grade 5 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2018, 2018 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 5012065: | Grade 4 Accelerated Mathematics (Specifically in versions: 2019 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 5012015: | Foundational Skills in Mathematics 3-5 (Specifically in versions: 2019 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
Related Resources
Formative Assessments
| Name | Description |
| The Odometer | Given an odometer reading, students are asked to discuss the value of each digit and explain how a digit in one place represents 10 times as much as the same digit to its right, and one-tenth as much as the same digit to its left. |
| Dylan’s Baseball Card Collection | Students are asked to find |
| Five-Tenths | Students are asked to consider how much larger five is than five-tenths. |
| Walking to School | Students are presented with two decimals in the context of a distance word problem and asked to tell how many times longer one distance is than the other. |
Lesson Plans
| Name | Description |
| Wire We All Wet? | A fire caused by faulty wiring set off a sprinkler system, which damaged a school. The school must be remodeled and the electrical wiring must be replaced. Students will decide which materials to use to as conductors and which to use as insulators in the new wiring. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Understanding Place Value | This lesson is designed to help students understand the 10 to 1 relationship among place value positions and the mathematical patterns when calculating place value. |
| "Shift the Place, Shift the Value" - Understanding Adjacent Places in the Base-ten System | In this lesson students will be challenged to discover the relationship between values of adjacent places in the base-ten system. After an introduction to the concept by the teacher, pairs of students will play a place value game with digit cards, then they will individually complete a written summative assessment. |
| The Dazzling Painting Co. | Students will read a letter from a painting company from New York who are planning to expand to Florida. They need help deciding on which paint sprayers to purchase. Students will use their understanding of rate and percentages to analyze data and make suggestions. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought processes. MEAs follow a problem-based, student-centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEAs visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Intro to Multiplying Decimals by 10, 100, 1000 | In this lesson, students are introduced to multiplying decimals by 10, 100, and 1000, in which students begin by creatively solving word problems. Students will analyze the number sentences used to solve the word problems, looking for and recording patterns and discovering that each place value has a value ten times as much as the place to its right, which is why each time a number is multiplied by 10, the digits move one place to the left. |

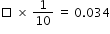
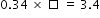
 of 500 and are assessed on the use of their knowledge of the base-ten number system.
of 500 and are assessed on the use of their knowledge of the base-ten number system.