General Information
Test Item Specifications
MA.912.G.2.7 Determine how changes in dimensions affect the perimeter and area of common geometric figures.
Students will solve problems by using and/or deriving formulas for perimeter and/or area of polygons.
Items requiring students to calculate area may require the use of the apothem.
Composite figures may include circles.
Items may be set in either mathematical or real-world contexts.
Graphics should be used in most of these items, as appropriate.
Sample Test Items (2)
| Test Item # | Question | Difficulty | Type |
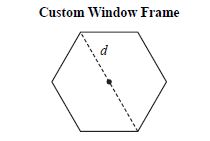
| Sample Item 1 | Marisol is creating a custom window frame that is in the shape of a regular hexagon. She wants to find the area of the hexagon to determine the amount of glass needed. She measured diagonal d and determined it was 40 inches. A diagram of the window frame is shown below. Which of the following is closest to the area, in square inches, of the hexagon? |
N/A | MC: Multiple Choice |
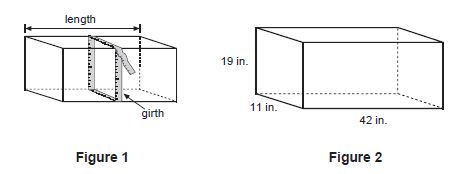
| Sample Item 2 | A package shaped like a rectangular prism needs to be mailed. For this package to be mailed at the standard parcel-post rate, the sum of the length of the longest side and the girth (the perimeter around its other two dimensions) must be less than or equal to 108 inches (in.). Figure 1 shows how to measure the girth of a package. What is the sum of the length, in inches, of the longest side and the girth of the package shown in Figure 2? |
N/A | FR: Fill-in Response |