General Information
Subject Area: Mathematics (B.E.S.T.)
Grade: 912
Strand: Data Analysis and Probability
Date Adopted or Revised: 08/20
Status: State Board Approved
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Exponential function
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
In Algebra I, students wrote exponential functions that modeled relationships characterized by having a constant percent of change per unit interval and found a line of fit for linear bivariate numerical data. In Math for College Liberal Arts, students recognize exponential functions by the constant percent rate of change per unit interval and fit exponential functions to appropriate bivariate numerical data. In other courses, students will use the logarithm to determine whether an exponential model is appropriate.- For students to have full understanding of exponential functions, instruction includes MA.912.AR.5.3, MA.912.AR.5.4, MA.912.AR.5.5 and MA.912.AR.5.6.
- Growth or decay of a function can be defined as a key feature (constant percent rate of change) of an exponential function and useful in understanding the relationships between two quantities.
- Instruction includes reviewing the exponential form () = (1 + ) where is the initial amount, is the growth rate, and is time.
- Instruction includes making predictions using the model. Students use interpolation, making predictions within the range of given data, and extrapolation, making predictions outside of the range of given data.
- For example, if students were collecting data on growth of humans between ages 0 to 5 on a scatter plot and wrote an exponential function representing the data. Interpolation would be predicting heights between the ages of 0 to 5. If students wanted to predict the heights of age 14, this would be extrapolation.
- Interpolation is often more accurate than extrapolation.
- Given our example above, a model could predict a height of 15 feet which would not be realistic within the given context.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students may confuse when an exponential function is needed, rather than a linear or quadratic function, given a table or written description.
- Students may not know the difference between interpolation (predictions within a data set) and extrapolation (predictions beyond a data set).
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.5.1, MTR.7.1)- Joshua is saving money in a savings account where interest is compounded yearly. The chart below shows how much is in Joshua’s account after a number of years.
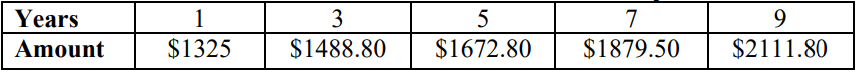
- Part A. What ratio describes how much Joshua’s amount increases each year?
- Part B. What does this ratio describe in this situation?
- Part C. How much did Joshua originally deposit in his account?
- Part D. Write an exponential function that describes the amount of money in his account after years.
- Part E. How much would be in his account after 10 years? 15 years?
- Part F. How would the function change if Joshua originally deposited $15,000? How much would he have in his account after 10 years?
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1- In the early 2000s the exponential equation = 1.4457(1.0137) was used to model the population of the world where represents the population, in billions of people, and represents the years since 1900.
- Part A. Based on the given equation, estimate the population in the year 2020.
- Part B. Is this model still representative of the population today?
