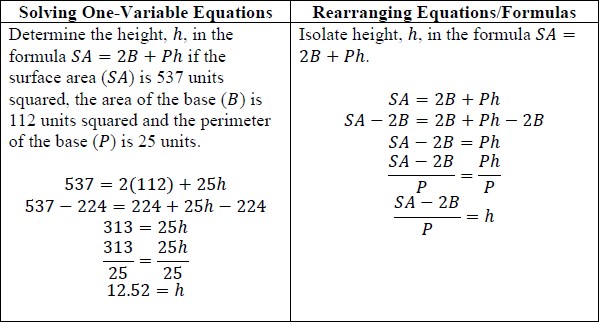
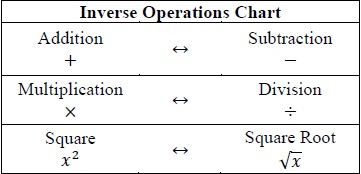
Rearrange equations or formulas to isolate a quantity of interest.
: Instruction includes using formulas for temperature, perimeter, area and volume; using equations for linear (standard, slope-intercept and point-slope forms) and quadratic (standard, factored and vertex forms) functions.
| Course Number1111 |
Course Title222 |
| 1200310: | Algebra 1 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1200320: | Algebra 1 Honors (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1200370: | Algebra 1-A (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1200380: | Algebra 1-B (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1200400: | Foundational Skills in Mathematics 9-12 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 7912080: | Access Algebra 1A (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2018, 2018 - 2019, 2019 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 7912090: | Access Algebra 1B (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2018, 2018 - 2019, 2019 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 1200315: | Algebra 1 for Credit Recovery (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1200375: | Algebra 1-A for Credit Recovery (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1200385: | Algebra 1-B for Credit Recovery (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2022, 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 7912075: | Access Algebra 1 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2018, 2018 - 2019, 2019 - 2022, 2022 and beyond (current)) |
| 1210305: | Mathematics for College Statistics (Specifically in versions: 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1200388: | Mathematics for Data and Financial Literacy Honors (Specifically in versions: 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 1200384: | Mathematics for Data and Financial Literacy (Specifically in versions: 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| 7912120: | Access Mathematics for Data and Financial Literacy (Specifically in versions: 2022 - 2023, 2023 and beyond (current)) |
| 1200710: | Mathematics for College Algebra (Specifically in versions: 2022 - 2024, 2024 and beyond (current)) |
| Name |
Description |
| Solving Formulas for a Variable | Students are given the slope formula and the slope-intercept equation and are asked to solve for specific variables. |
| Solving Literal Equations | Students are given three literal equations, each involving three variables and either addition or subtraction, and are asked to solve each equation for a specific variable. |
| Literal Equations | Students are given three literal equations, each involving three variables and either multiplication or division, and are asked to solve each equation for a specific variable. |
| Solving a Literal Linear Equation | Students are given a literal linear equation and asked to solve for a specific variable. |
| Surface Area of a Cube | Students are asked to solve the formula for the surface area of a cube for e, the length of an edge of the cube. |
| Rewriting Equations | Students are given a literal equation involving four variables and are asked to solve for the variable in the quadratic term. |
| Name |
Description |
| Filled to Capacity! | This is a lesson where students investigate, compare, dissect, and use the relationship between volume of a cone and cylinder with equal corresponding dimensions. |
| My Geometry Classroom | Students will learn how to find the area and perimeter of multiple polygons in the coordinate plane using the composition and decomposition methods, applying the Distance Formula and Pythagorean Theorem. Students will complete a Geometry Classroom Floor Plan group activity. Students will do a short presentation to discuss their results which leads to the realization that polygons with the same perimeter can have different areas. Students will also complete an independent practice and submit an exit ticket at the end of the lesson. |
| Free Fall Clock and Reaction Time! | This will be a lesson designed to introduce students to the concept of 9.81 m/s2 as a sort of clock that can be used for solving all kinematics equations where a = g. |
| Find your Formula! | Students will investigate the formula for the volume of a pyramid and/or cone and use those formulas to calculate the volume of other solids. The students will have hands-on discovery working with hollow Geometric Solids that they fill with dry rice, popcorn, or another material. |
| Ranking Sports Players (Quadratic Equations Practice) | In this Model Eliciting Activity, MEA, students will rank sports players by designing methods, using different indicators, and working with quadratic equations.
Model-Eliciting-Activities, MEAs, allow students to critically analyze data sets, compare information, and require students to explain their thinking and reasoning. While there is no one correct answer in an MEA, students should work to explain their thinking clearly and rationally. Therefore, teachers should ask probing questions and provide feedback to help students develop a coherent, data-as-evidence-based approach within this learning experience. |
| My Favorite Slice | The lesson introduces students to sectors of circles and illustrates ways to calculate their areas. The lesson uses pizzas to incorporate a real-world application for the of area of a sector. Students should already know the parts of a circle, how to find the circumference and area of a circle, how to find an arc length, and be familiar with ratios and percentages. |
| Acceleration | In this lesson students will learn to:
- Identify changes in motion that produce acceleration.
- Describe examples of objects moving with constant acceleration.
- Calculate the acceleration of an object, analytically, and graphically.
- Interpret velocity-time graph, and explain the meaning of the slope.
- Classify acceleration as positive, negative, and zero.
- Describe instantaneous acceleration.
|
| Falling for Gravity | Students will investigate the motion of three objects of different masses undergoing free fall. Additionally, students will:
- Use spark timers to collect displacement and time data.
- Use this data to calculate the average velocity for the object during each interval.
- Graph this data on a velocity versus time graph, V-t. They find the slope of this graph to calculate acceleration.
- Calculate the falling object's acceleration from their data table and graph this data on an acceleration versus time graph, a-t.
- Use their Spark timer data paper, cut it into intervals, and paste these intervals into their displacement versus time graph.
|
| Efficient Storage | The topic of this MEA is work and power. Students will be assigned the task of hiring employees to complete a given task. In order to make a decision as to which candidates to hire, the students initially must calculate the required work. The power each potential employee is capable of, the days they are available to work, the percentage of work-shifts they have missed over the past 12 months, and the hourly pay rate each worker commands will be provided to assist in the decision process. Full- and/or part-time positions are available. Through data analysis, the students will need to evaluate which factors are most significant in the hiring process. For instance, some groups may prioritize speed of work, while others prioritize cost or availability/dependability.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Graphing vs. Substitution. Which would you choose? | Students will solve multiple systems of equations using two methods: graphing and substitution. This will help students to make a connection between the two methods and realize that they will indeed get the same solution graphically and algebraically. Students will compare the two methods and think about ways to decide which method to use for a particular problem. This lesson connects prior instruction on solving systems of equations graphically with using algebraic methods to solve systems of equations. |
| Math in Mishaps | Students will explore how percentages, proportions, and solving for unknowns are used in important jobs. This interactive activity will open their minds and address the question, "When is this ever used in real life?" |
| Don't Take it so Literal | The purpose of this lesson is to have students practice manipulation of literal equations to solve for the variable of interest. A literal equation is an equation that has more than variable (letter). |
| Survey Says... We're Using TRIG! | This lesson is meant as a review after being taught basic trigonometric functions. It will allow students to see and solve problems from a real-world setting. The Perspectives video presents math being used in the real-world as a multimedia enhancement to this lesson. Students will find this review lesson interesting and fun. |
relating to the translational of motion, where d represents distance,
solve for the radius

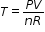 to isolate temperature as the quantity of interest.
to isolate temperature as the quantity of interest. 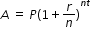 , solve for P.
, solve for P. 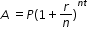 , solve for t.
, solve for t.