Interpret numerical data, with whole-number values, represented with tables or line plots by determining the mean, mode, median or range.
Rain was collected and measured daily to the nearest inch for the past week. The recorded amounts are 1,0,3,1,0,0 and 1. The range is 3 inches, the modes are 0 and 1 inches and the mean value can be determined as
of an inch. This mean would be the same if it rained
of an inch each day.
Instruction includes interpreting the mean in real-world problems as a leveling out, a balance point or an equal share.
| Name |
Description |
| How Generative AI like ChatGPT Works | Students will explore Artificial Intelligence (AI) and how generative AI models use Large Language Models (LLMs) and Natural Language Processing NLP to generate outputs. This grades 4-5 lesson is an integrated Computer Science, ELA and Math lesson designed for application of math and ELA content knowledge while exploring and using computational thinking to understand how generative AI works, making cross-curricular connections to understand emerging technologies. |
| Voting Rights Amendments: The Voting Rights Act of 1965 | In this lesson plan, students will create and analyze a line graph to explore how the Voting Rights Act of 1965 expanded civic participation. |
| Voter Turnout and the 26th Amendment | In this lesson plan, students will graph and interpret voter turnout data to explain how the 26th Amendment expanded the opportunity for civic participation. |
| Voter Turnout and the 24th Amendment | Students will use voter turnout data to create and analyze a line graph to explain how the 24th Amendment expanded civic participation in this integrated lesson plan. |
| Practicing With Mean | In this lesson plan, students will practice finding the mean of a set of data and be able to connect that to how mean is used in real-life. Students will be able to collect data, create line plots, interpret the data, and find the mean. |
| Voter Task Force | Students will help the Supervisor of Elections determine which voter registration locations could be improved to help more citizens get registered to vote. Students will learn about the number of citizens who registered to vote in a general election year compared to the total population of those eligible to vote. They will discuss which voter registration locations will provide the most access to citizens and allocate funds to help address the issue in this modeling eliciting activity.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom.
|
| Voter Turnout and the 19th Amendment | Students will graph and analyze voting data to explain how the 19th Amendment expanded civic participation in this lesson plan. |
| Voter Turnout and the 15th Amendment | In this lesson plan, students will graph and analyze voting data to explain how the 15th Amendment expanded civic participation. |
| How Does Force Affect Motion? | Students will explore how force affects an object's motion. Students will discuss how the greater the mass of an object, the greater the force required to move an object. Students will use data gathered through experimentation to justify their reasoning and understanding of forces and motion. |
| Marbelous Pool Noodle Ramps | In this lesson, students will build a ramp out of a pool noodle and use it to launch a marble across the room. Students will investigate by adjusting the height and slope of the ramp and record their findings on a data sheet. Students will practice collecting and analyzing data and will investigate the importance of performing repeated experimental trials. Students will practice converting metric units of distance as well as the addition and division of decimals to find the mean of a small data set. |
| Paper Airplanes Away! | In this lesson, students will design and fly their own paper airplane and analyze their flight data to determine the best designs for getting planes to travel the farthest distance. Students will organize class flight data into a line plot and calculate the mean, median, mode, and range for the data set. |
| Fly Runners Order of Operations MEA | In this Model Eliciting Activity, MEA, the students will determine the best ad for a tennis shoe company.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Camping Supply Innovators MEA | In this Model Eliciting Activity, MEA, the students' will determine the best canteen for an outdoor hiking company.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Fast Food Decision | Students will rank fast food restaurants from best to worst based on their nutrition, price, and distance to sport field. Students will have to make tradeoffs for nutrition or price.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Getting Dry | This MEA asks the students to compare hand drying products based on: initial cost, replacement cost and absorbency. Students will provide the "top choice" to the principal of the school and explain how they arrived at the solution. In the twist, students will be asked to consider the environmental impact of the products and reevaluate their conclusions.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought processes. MEAs follow a problem-based, student-centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEAs visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| New Frozen Yogurt Store | This MEA asks students to decide which factors are important in developing a successful frozen yogurt (froyo) store in order to compete with and become the best store in the area. Students will provide feedback to an entrepreneur who is looking to open a frozen yogurt store. They will rank order their choices of the most successful to least successful store. Students will provide a detailed written explanation for how they decided to rank factors and their solution rating existing stores from best to worst.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought processes. MEAs follow a problem-based, student-centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEAs visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |


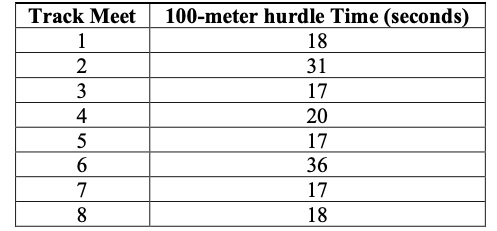
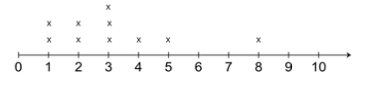

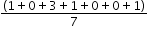 which is equivalent to
which is equivalent to 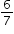 of an inch. This mean would be the same if it rained
of an inch. This mean would be the same if it rained