General Information
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Expression
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is for students to translate between numerical and written mathematical expressions. This builds from previous work where students wrote equations with unknowns in any position of the equation in grade 4 (MA.4.AR.2.2). Algebraic expressions are a major theme in grade 6 starting with MA.6.AR.1.1.- During instruction, teachers should model how to translate numerical expressions into words using correct vocabulary. This includes naming fractions and decimals correctly. Students should use diverse vocabulary to describe expressions.
- For example, in the expression 4.5 + (3 × 2) could be read in multiple ways to show its operations. Students should explore them and find connections between their meanings (MTR.3.1, MTR.4.1, MTR.5.1).
- 4 and five tenths plus the quantity 3 times 2
- 4 and 5 tenths plus the product of 3 and 2
- The sum of 4 and 5 tenths and the quantity 3 times 2
- The sum of 4 and 5 tenths and the products of 3 and 2
- For example, in the expression 4.5 + (3 × 2) could be read in multiple ways to show its operations. Students should explore them and find connections between their meanings (MTR.3.1, MTR.4.1, MTR.5.1).
- The expectation of this benchmark is to not use exponents or nested grouping symbols. Nested grouping symbols refer to grouping symbols within one another in an expression, like in 3 + [5.2 + (4 × 2)].
- Instruction of this benchmark helps students understand the order of operations, the expectation of MA.5.AR.2.2.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students can misrepresent decimal and fraction numbers in words. This benchmark helps students practice naming numbers according to place value.
- Some students can confuse the difference between what is expected in the expressions 5(9 + 3) and 5 + (9 + 3). Students need practice naming the former as multiplication (e.g., 5 times the sum of 9 and 3) and understanding that in that expression, both 5 and 9 + 3 are factors.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
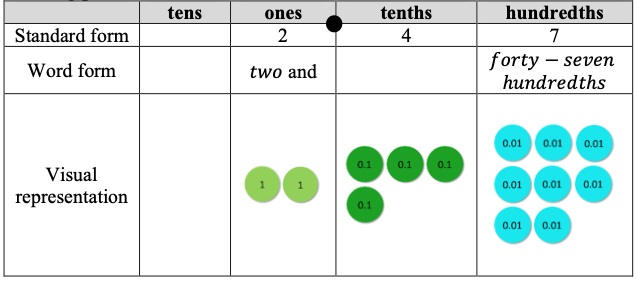
- Instruction includes opportunities to name fractions and decimals correctly according to place value. The teacher provides students a place value chart to support correctly naming decimals. Students use appropriate terminology for naming fractions.
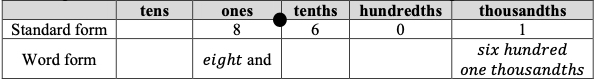
- For example, students write 10.36 in standard form and word form in a place value chart.
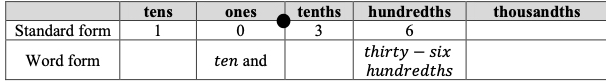
- For example, students write 2.47 in standard form and word form in a place value chart using place value disks.
- For example, students write in word form (five twelfths).
- For example, students write 2 in word form (two and seven eighths). This is repeated with additional fractions and decimals.
- Instruction includes opportunities to correctly translate numerical expressions into words
using appropriate vocabulary.
- For example, the teacher has students read aloud the following expression and write in word form. Next, the teacher models one way of reading aloud and has students provide alternate ways while using questioning to facilitate the conversation about the multiple ways the expression can be read aloud to show its operations.
- Eighteen and forty-nine hundredths minus the quotient of twenty-seven divided by three.
- 18 and 49 hundredths minus the quantity 27 divided by 3.
- The difference between 18 and 49 hundredths and the quotient of 27 divided by 3.
- The difference between 18 and 49 hundredths and the quantity 27 divided by 3.
- For example, the teacher models how to translate the expression 5(9 + 3) into words (e.g., 5 times the sum of 9 and 3) and explains that in this expression, both 5 and 9 + 3 are factors.
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.4.1)
- Nadia sees the numerical expression 6.5 + (4-2). She translates the expression as, “6 and five tenths plus 1 half times 4, minus 2."
- Part A: Is her translation correct? Explain.
- Part B: Evaluate the expression.
Instructional Task 2 (MTR.3.1)
Translate the written mathematical description below into a numerical expression: Divide the difference of 20 and 5 by the sum of 4 and 1.
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1
Translate the numerical expression below into a written mathematical description.
Instructional Item 2
Translate the written mathematical description into a numerical expression. “one half the difference of 6 and 8 hundredths and 2”*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.
