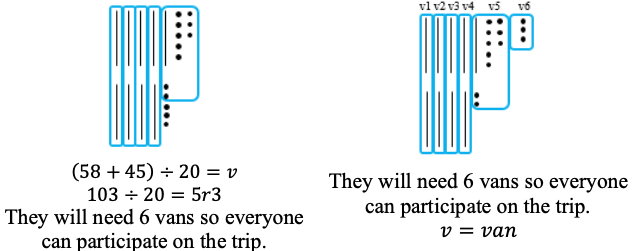
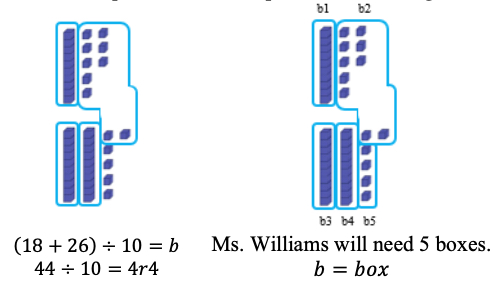
Solve multi-step real-world problems involving any combination of the four operations with whole numbers, including problems in which remainders must be interpreted within the context.
Depending on the context, the solution of a division problem with a remainder may be the whole number part of the quotient, the whole number part of the quotient with the remainder, the whole number part of the quotient plus 1, or the remainder.
| Name |
Description |
| Disaster Relief | Students will analyze data to develop a resupply schedule for a humanitarian mission following a natural disaster. They will apply mathematical operations over multiple steps to minimize the operational cost of the humanitarian mission.
This is an open-ended engineering design lesson where students will develop a model to help them solve a problem. There are no “right” answers as the lesson is focused on the process of developing a solution and the skills and reasoning behind the process. Students should be given the freedom to interpret the problem and parameters in unique ways to pursue their own lines of thinking in producing a solution. |
| Paying for Payloads | Students will investigate the relationship between mass and the force required to lift an object, as well as the impact of forces on the object’s motion. Using payload data and rocket specs, they will develop a plan with a budget to launch five modules of a new spaceport into low Earth orbit. |
| Solving Multi-Step Word Problems With "Undecided" Colonists | Students will be divided into groups and given a set of multi-step real-world problems to solve. The word problems will be specific to topics important to the neutral colonists during the American Revolution. The lesson will conclude with a class discussion of the word problems tying the math and civics together in this integrated lesson plan. |
| Solving Multi-Step Word Problems with Loyalists and Patriots | Students will be divided into groups and given a set of multi-step real-world problems to solve. The word problems will be specific to topics important to the Loyalists during the American Revolution. The lesson will conclude with a class discussion of the word problems tying the math and civics together in this integrated lesson plan. |
| Solving Real-World Problems P-3 | This integrated lesson includes students practicing multistep problem-solving while analyzing the mathematical thinking of others and justifying their results by explaining methods and processes. Students will work in groups to solve a real-world problem, involving a citizenship context, by using a strategy of their choice. As a class, the students will analyze the different ways the remainder can be interpreted based on different questions involving the same context.
|
| Solving Multi-Step Word Problems With Patriots and Loyalists | Students will be divided into groups and given a set of multi-step real-world problems to solve. The word problems will be specific to topics important to the Patriots during the American Revolution. The lesson will conclude with a class discussion of the word problems tying the math and civics together in this integrated lesson plan. |
| Solving Real-World Problems P-2 | This integrated lesson includes students solving multi-step real-world word problems using the four operations. Students will solve word problems involving citizen’s duties and responsibilities by using a strategy of their choice and analyzing the context to interpret remainders. |
| Solving Real World Problems P-1 | Students will be exposed to several word problems involving citizens' duties and responsibilities, guiding them to reflect on what could happen if citizens do not fulfill their responsibilities. As the lesson progresses, the students will learn to combine addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division to solve multistep word problems in this integrated lesson plan. |
| Gimme Two Steps! | In this lesson, students will create representations for different multi-step word problems. One of these representations will be an expression with a variable. |
| Blessings in a Bag!! | In this MEA, the students will help a charitable organization select 5 snack items from a list to provide nutritious snacks for children in low-income communities. Students will practice using the four operations to solve real-world problems and use decimal notation to make calculations involving money. Additionally, they will be asked to compare multi-digit numbers to the thousandths. |
| Getting the Top Mini-Fridge not a Small Deal | In this MEA, students will create a procedure to rank five mini-refrigerators to determine which one should be purchased for the school by the PTA based on size, type, features, energy usage, and cost. In the process, students will solve real-world problems involving the multiplication of multi-digit numbers with decimals to the hundredths, including using money. Students will also determine the volume of a rectangular prism using a formula. |
| Textbook Predicament | In this Model Eliciting Activity, MEA, students multiply and compare information to provide the most appropriate textbook for a county.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Museum Dilemma | In this MEA, students evaluate the contributions of various explorers to help a museum select the subject who provided the most impact on Western development for a new exhibit. Students will need to convert units to have the necessary information to help come up with a solution to the problem. |
| One Step at a Time: Word Problems | In this lesson, students will use the four operations to solve multi-step word problems composed of whole numbers. Students will be asked to estimate, write equations, decide if their answers are reasonable, and explain their decision. Several problems include explaining the meaning of the remainder in a division problem. |
| Birthday Balloon Planner | In this Model Eliciting Activity, MEA, students will develop a procedure for choosing a balloon company for a birthday party and rank them from best to worst.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student-centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Party Planners Wanted | In this Model Eliciting Activity, MEA, students will work in collaborative groups to solve multistep problems with whole numbers and decimals by using different mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. The students will be asked to assist a businessman who is planning a party for his employees. They will need to read several ads and decide which company offers the best deal in renting tables, chairs, and tablecloths for the client. They will need to take into consideration the number of guests attending the party and the budget allowed. A twist is added to the problem when the students are asked to consider an additional ad and the fact that the guest list is now slightly larger.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student-centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Cameras on Campus | In this MEA, students will interpret data related to digital cameras to make a recommendation for a school to purchase for students to use.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Which Food Should I Feed My Cat? | The students will convert fractions into decimals and multiply to determine the amount of food to feed their assigned cat. Using this amount, they will calculate (division of decimals) the number of servings and the price per serving of cat food. Students will work with three brands of food and enter the data into their charts. Finally, the students will analyze the data to determine the most affordable food. |
| Diving deeper into division | This lesson introduces students to dividing with 2 digit divisors. Students are asked to apply strategies that they learned in dividing with 1 digit divisors such as partial quotients or breaking numbers apart using the distributive property. |
| Wallpaper Woes Money Math: Lessons for Life | Students hear a story about a middle-school student who wants to redecorate his bedroom. They measure the classroom wall dimensions, draw a scale model, and incorporate measurements for windows and doors to determine the area that could be covered by wallpaper. Students then hear more about the student's redecorating adventure and learn about expenses, budget constraints, and tradeoffs. |
| New Coat of Paint | In this Model Eliciting Activity, MEA, students will work in collaborative groups to solve multistep problems with whole numbers using the 4 operations. The students will be asked to assist a property owner, who is planning to repair his new property, in purchasing the right exterior paint. They will need to read a data table, rank the paints from highest to lowest, calculate the amount of gallons needed according to the surface area, and calculate the total cost of each paint. A twist is added to the problem when one of the paints is not available, but two others are added, and also the owner wants to paint the rectangular area of the dividing walls outside.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student-centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Rockin' Remainders | This is a lesson designed to teach interpreting remainders in division based on the context of the word problem. Included with the lesson plan is a PowerPoint for direct instruction and word problems for small group or individual practice. |
| Those Pesky Remainders | This is a lesson to help students understand how to interpret the remainder in a division problem. Real world problems are presented in a PowerPoint so students may visualize situations and discover the four treatments of a remainder. |