General Information
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- NA
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
- NA
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is to connect concepts of unit conversions to time and distance and solve problems with these conversions. In grade 3, students solved one- and two-step elapsed time problems without converting units of time or crossing from a.m. to p.m. or p.m. to a.m. (MA.3.M.2.2).- For distance problems, students may need to understand multiplicative comparison (e.g., 20 is twice as many as 10).
- For instruction, an open number line is a strategy students can use to solve elapsed time problems.
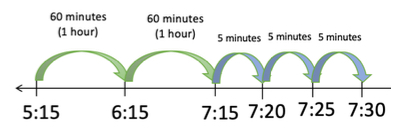
- Students need to spend time solving problems crossing between a.m. and p.m., and vice- versa.
- Students should also have a firm understanding of the terms quarter hour (15 minutes) and half hour (30 minutes).
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students can confuse when time crosses the hour because it does not follow the base-ten pattern where they are familiar. For example, students can misinterpret that the elapsed time between 9:55 a.m. and 10:05 a.m. and state that the elapsed time is 50 minutes because they have found the difference from 55 to 105. The use of number lines and clocks side-by-side help students build understanding about how elapsed time is calculated.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
- Instruction includes the use of number lines and clocks side-by-side to help students build understanding about how elapsed time is calculated.
- Instruction includes using a number line and counting by ones to demonstrate what happens when time crosses the hour because it does not follow the familiar base ten pattern.
- For example, use a number line to find the elapsed time between 9:55 a.m. and 10:05 a.m. and explain what happens when time crosses the hour at 10:00 a.m.
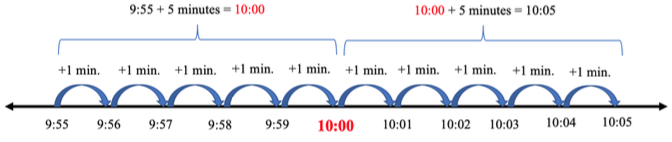
- Instruction includes demonstrating what happens when time crosses the hour because it does not follow the familiar base ten pattern.
- For example, instruction may include using a geared manipulative (Judy) clock to find the elapsed time between 9:55 a.m. and 10:05 a.m. Students move the minute of the hand one minute at a time from 9:55 to 10:00. After each minute, the teacher asks the students to record what time it is. The teacher has students pay special attention to what happens when the minute hand moves from 9:59 to the next minute.
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.7.1)
Steve drove 2,465 miles away to college. On Parents’ Weekend, his parents drove the distance round trip from home, with an additional 385 miles traveled to visit his sister on their return trip. How many total miles did his parents drive on Parents’ Weekend?
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1
After lunch, Billy walked the dog for 17 minutes and then immediately after, did his chores for 58 minutes. If he finished his chores at 12:15 p.m., what time did he start walking the dog?- a. 1:30 p.m.
- b. 1:13 p.m.
- c. 11:17 a.m.
- d. 11:00 a.m.
*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.
