General Information
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Equation
- Expression
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is to determine if students can connect their understanding of using the four operations fluently (MTR.3.1) to the concept of the meaning of the equal sign. This concept builds on the understanding of determining if addition and subtraction equations (MA.2.AR.2.2) and multiplication and division equations (MA.3.AR.2.2) are true and false.- Students will determine if the expression on the left of the equal sign is equivalent to the expression to the right of the equal sign. If these expressions are equivalent, then the equation will be deemed true.
- Students may use comparative relational thinking or estimation, instead of solving, to determine if the equation is true or false.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Many students have difficulty understanding that the equal sign is a relational symbol. They believe that the equal sign makes the expression on the right side of the equation equal to the expression on the left side so that all equations would be true. Instead an equation with an equal sign can be true or false, depending on whether the expressions on each side of the equal sign are equal to each other or not.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
- Instruction includes opportunities to explore the meaning of the equal sign. The teacher provides clarification that the equal sign means “the same as” rather than “the answer is,” providing multiple examples for students to evaluate equations as true or false using the four operations with the answers on both the left and right side of the equation. The teacher begins by using single numbers on either side of the equal sign to build understanding and uses the same equations written in different ways to reinforce the concept.
- For example, the teacher shows the following equations. Students are asked if they are true or false statements and to explain why. This is repeated with additional true and false equations using the four operations.
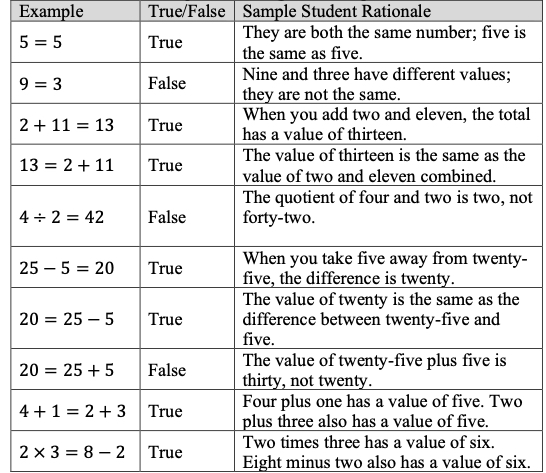
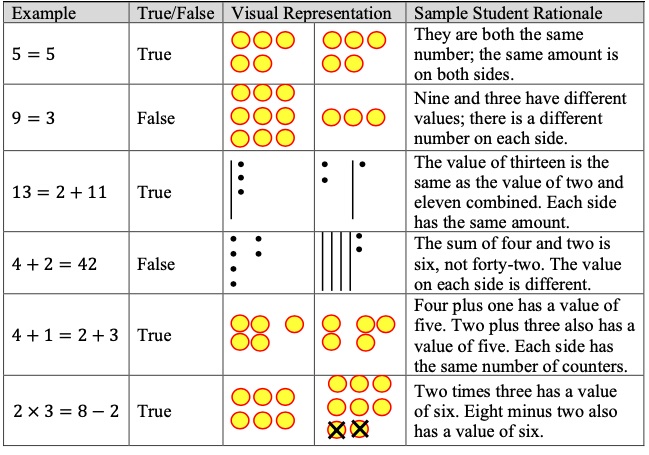
- Teacher provides opportunities to explore the meaning of the equal sign using visual representations (e.g., counters, drawings, base-ten blocks) on a t-chart to represent the equations. The teacher provides clarification that the equal sign means “the same as” rather than “the answer is,” and provides multiple examples for students to evaluate equations as true or false using the four operations with the answers on both the left and right side of the equation. The teacher begins by using single numbers on either side of the equal sign to build understanding, using the same equations written in different ways to reinforce the concept.
- For example, the teacher shows the following equations. Students use counters, drawings, or base-ten blocks on a t-chart to represent the equation. The teacher asks students if they are true or false statements and to explain why. This is repeated with additional true and false equations using the four operations.
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1
Using the numbers below, create an equation that is true.
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1
Determine whether the equation below is true or false.*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.
