General Information
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- Dividend
- Divisor
- Expression
- Equation
- Quotient
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is for students to choose a reliable method for dividing 4-digit numbers by 1-digit numbers. It builds on the understanding developed during exploration (MA.3.NSO.2.2) and on automaticity (MA.4.NSO.2.1), and prepares for procedural fluency (MA.5.NSO.2.2).- This benchmark connects to previous work with division within 144. Before achieving procedural reliability it may be useful for students to engage in additional exploratory work dividing multi-digit numbers by single-digit numbers. Students should use multiple methods (MTR.2.1) such as area models or models of base-ten blocks to connect understanding to a method they will use with procedural reliability and ultimately leading to a standard algorithm.
- Base-Ten Blocks
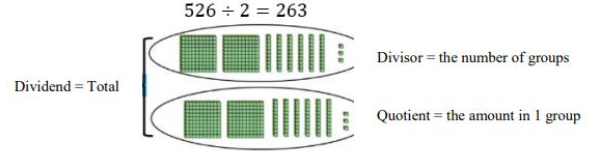
- Long Division Algorithm
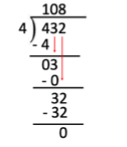
- Area Model
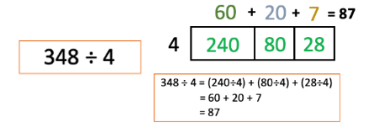
- Partial Quotient Division

- When students are using their preferred method they should be able to explain their thinking, connecting it to place value understanding and the relationship between division and repeated subtraction.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Many students are taught an algorithm for division and then tend to look at the digits within the number as single digits instead of thinking about the place value of each digit or thinking about the number as a whole. When asked if their solution is reasonable, students do not understand what is reasonable because they are unable to estimate since they do not see the number in its entirety, but rather, as individual digits. Students must have a solid understanding about place value and the properties of operations to make sense of division.
- Some students may not understand that the remainder represents a fraction with the divisor as the denominator. For example, 7 ÷ 3 = 2r1 means that 7 ÷ 3 = 2 . Students should have experience with equal sharing division problems that involve remainders (MA.4.AR.1.1).
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
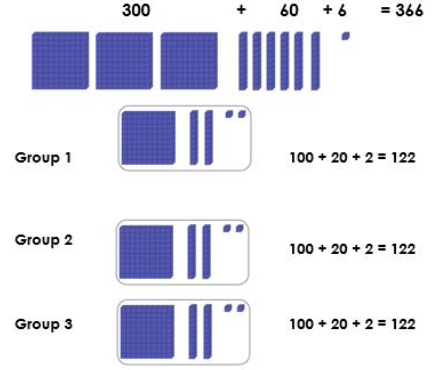
- Instruction includes connecting place value with the partial products model. Students should not view the digits as individual numbers but connect individual digits with the value of that number.
- Example: 366 is 300 + 60 + 6.
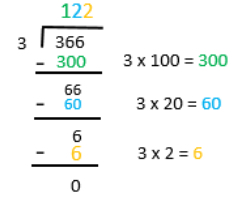
- Instruction includes problems involving division with a remainder. Students use models to understand what the remainder is. The remainder can be written as a whole number or a fraction.
- For example, Karly, Juan, and Li share 4 cookies equally. How many cookies can each person eat? Karly, Juan, and Li each can eat one whole cookie but then must split the 4th cookie into thirds so that they can each eat 1 .The remainder 1 in this division problem represents the fraction .
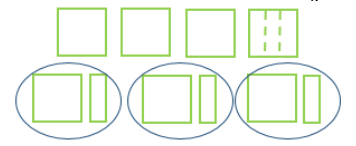
- Instruction connects place value to dividing whole numbers equally. Students build the number with base ten blocks and then physically divide the number into equal groups.
- For example, when solving 366 ÷ 3, students should build the number 366 and then physically move the blocks into 3 equal groups. This will help solidify the understanding from thinking of the digit as a “3” and now thinking about it as 300.
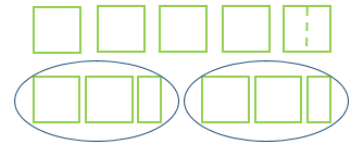
- Instruction includes the opportunity to use models to understand what the remainder is. The remainder can be written as a whole number or a fraction. Students physically cut or break apart paper to show what is happening in problems involving remainders.
- For example, using the problem: Frank and Lisa share five brownies. How many brownies can they each eat? Students should model the problem with five pieces of paper, each representing one brownie. Students should start by labeling each brownie. Frank and Lisa each have two brownies with one brownie left over. Then, students physically cut the last brownie into two equal parts so that each person is able to eat 2 brownies. Relate this to an equation 5 ÷ 2 = 2 .
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.5.1)
Using only the number tiles 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 or 7, fill in the blanks in the division situation to find a quotient as close to 100 as possible.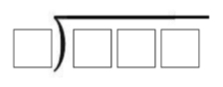
Instructional Task 2 (MTR.7.1)
Sam and Sally were given $117 after they helped deliver groceries for a month. In order to split the money equally, Sam divides 117 by 2 and gets 58 with a remainder of 1. Explain how they should use this result to determine their equal shares in dollars and cents.
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1
What is 1,545 divided by 5?
Instructional Item 2
What is 311 divided by 7? (Express the remainder as a fraction)*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.
