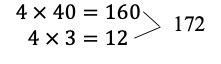Multiply two whole numbers, up to three digits by up to two digits, with procedural reliability.
Instruction focuses on helping a student choose a method they can use reliably.
| Name |
Description |
| Order_in_the_School_Zone_Part_3 | Students will work in pairs or small groups. They will be provided with a “school district” and zones. The groups will be tasked with assigning each zone to a school, while respecting the school's enrollment caps and the zone's proximity to the school. Once the zones are assigned, the students will calculate the approximate busing costs. Then, the groups will pair off and compare how they determined zoning for each school. |
| Order_in_the_School_Zone_Part_2 | Students will determine the number of students from each zone that would need buses to get to their new schools. Then they will determine the total cost of transportation per week, per month and per school year. Students will discuss the possibility of adding portable classrooms instead of rezoning and comparing the cost. They will discuss how this cost increase could affect the school budgets and how the students and families could work with the school board on alternative solutions, in this integrated lesson plan. |
| Emergency Savings | Students will use their multiplication skills to explore the importance of taxes and how the government uses tax revenues to save for unforeseen emergencies, in this integrated lesson plan. |
| Plastic Footprint Lesson Plan | Students explore the problem of marine debris and ways that citizens can work alongside government to reduce the impact of plastic pollution. They calculate their plastic footprint by estimating the number of common single-use plastics they use in one year, then calculate how much plastic waste could be eliminated by cutting down on their use of single-use plastics in this integrated lesson plan. |
| Model Multiplication | This concept based, hands-on lesson is intended to help you assess how well your students understand and can use a variety of strategies and representations of 2 two-digit multiplication. |
| New Puppy's Pen | The purpose of this lesson is to help students find the missing side's length for rectangular area problems, when the total area and one side's length is given. The use of square tiles, then graph paper and equations are used throughout the lesson to help students progress from conceptual to procedural knowledge. |
| Modeling Multiplication for Mastery | In this lesson, students will work to multiply multi-digit numbers using various strategies. The lesson begins with a review of single x single digit numbers and progresses to two-digit x two-digit numbers. Students will use arrays, array frames with base ten blocks, and area models to explore and justify their solutions. |
| Multi-digit Multiplication Using Array Frames | This is an introductory lesson and is limited to multiplication of two-digit by one-digit numbers. The students will work with base ten blocks to model their multiplication. |
| Draw a blueprint of your dream house floor plan. | This lesson will help your students learn about area and perimeter while imagining and drawing a blueprint of their dream house floor plan. They will have so much fun drawing and creating their blueprint they will forget that they are actually learning how to find area and perimeter. |
| Hooray for arrays! | Students will identify prime and composite numbers through arrays. The lesson begins with a fun situational story. |
| Oops! What did I do? | This lesson uses a discovery approach to exploring different errors in various strategies of multiplication. The goal is to help students understand multiplication, not force them into using every strategy. |
| Multiplying Around the Block | The students will build upon their understanding of the place-value system and multiplying using base-ten models to build their understanding of multiplying with two-digit by two-digit numbers using area models. They will work with partners during the learning process to help them develop the usage of mathematical language when explaining their thinking and calculations to others. |
| Cupid's Carnival Rides | In this Model Eliciting Activity, MEA students will analyze different carnival rides to determine which ride would make the most profit by looking at factors such as number of tickets per ride, the cost per ticket, the length of the ride, the number of hours the ride is open, and the cost to operate the ride. Students will need to use different operations in order to solve the tasks and will be required to do multi-steps. |
| Robotics on a Budget | The P.T.A. President at ABC Elementary needs your students' help in selecting a robotics model that fits the needs of the students and the after school enrichment program. There is a budget of $2,000 that the students must adhere to. Students will be asked rank 4 models based on criteria given to them and the budget. Students will be given a data set to help them develop a procedure for doing so. In their teams they will write a letter to the P.T.A President giving their procedures and explanation of the strategy they used. Students will practice adding, subtracting and multiplying numbers to the thousands in order to calculate the amount of models that can be bought of a certain model without going over the budget. Rubrics are included to help grade students.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| The Dock at Lake Wonder MEA | In this Model Eliciting Activity, MEA, students will be asked to rank and choose from the potential docks the Lake Wonder Camp could purchase before next summer based on the data given. In the process, students will need to find area and perimeter as part of their criteria for ranking. The data provided is: dock dimensions, price per square foot for materials, warranty, and material quality. In the twist, students will be asked to calculate the cost of adding a safety bumper around each dock (after finding the perimeter) and calculate the total cost of each dock with the price of the safety bumper added. They must also stay within a $5,000 budget. Students must decide how to change their procedure with the new information.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student-centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Let's Think in Small Units | In this lesson students will make and complete tables to express larger unit measurements in terms of a smaller unit within one system of units. They will use the chart to make comparisons and explain their reasoning. |
| 2-Digit Array Multiplication | This lesson explores a conceptual approach to multiplying two 2-digit numbers. Students will create, explore, describe and record arrays built with place value pieces. The lesson supplies the understanding that will make multiplying multidigit numbers easy to do. |
| Amazing Arrays 3X1 or 1X3 | This lesson is the third lesson in a unit beginning with Amazing Arrays and Amazing Arrays 2X1.
In this lesson students solve a multiplication problem by drawing arrays and segment the areas in several ways to solve the problem. Students will also apply the distributive property, explore rotations of area models to demonstrate the commutative property of multiplication, and match a word problem with its array. |
| Boxing Math - Using the Area Model for Multiplication | A common mistake students make when learning to multiply is treating multiplication like addition, and multiplying ones by ones and tens by tens. In this lesson, your students will avoid that mistake as they learn to use the area model to do double digit multiplication. After group practice, students are taught a game to reinforce their learning. |
| Cookies and Treats | Fourth graders will help Cookies and Treats find cost-effective and eco-friendly packaging for its cookies. Students will organize data and compare prices using decimal notation in order to develop a procedure for choosing packaging for cookies. Students will use multiplication and division of whole numbers to plan for how many packages to order. Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Amazing Arrays 2X1 | This is a hands-on lesson for extending and practicing drawing arrays using area models that show a 2-digit number times a 1-digit number. Students are also required to use the distributive property of multiplication and the equations they represent. |
| Array for Charity! | Students will use array frames to find out how many pennies each of the classes in their school collected for a charity drive. Students will demonstrate and explain the array frame as well as determining how many pennies will go to each of the seven charities for which they have collected pennies. This lesson may be used as part of an introduction to multiplying 2-digit x 2-digit numbers. |
| Party Entertainment | In this MEA, students will decide which entertainer an owner of an entertainment company should hire. They will base their decisions on information provided on resumes. Students will calculate the cost of hiring the entertainer (multiplication of whole numbers) as well as compare the statistics of their talent competitions and attendance turn-out (comparing fractions). Students will write letters to the owner of the entertainment company ranking the entertainers and providing explanation and justification of their strategy for doing so.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Name |
Description |
| Multiplying: how to use the area model | In this video tutorial from Khan Academy, view a demonstration of how to set-up an area model for multiplying a two-digit number by a two-digit number on graph or grid paper and then link this to the standard algorithm. |
| Multiplying: 2-digit number times a 2-digit number (area model) | In this tutorial video from Khan Academy, view an example of how to multiply a two-digit number by a two-digit number using the area model. The video makes a connection between partial products and the area model. |
| Multiplying: 2-digit number times 2-digit number (using distributive property) | In this video tutorial from Khan Academy, view an example and a description of how the distributive property can be used to multiply a two-digit number by a two-digit number. The second example uses the area model with the distributive property. |
| Multiplying: 4-digits times 1-digit (using expanded form) | In this Khan Academy video tutorial, view an example of multiplying a 4-digit number by a 1-digit number by expanding the 4-digit number and multiplying by each digit individually in an area model. This video will help to build an understanding before teaching the standard algorithm. Multiplying with a 4-digit factor is larger than some standards which limit factors to 3-digits. |
| Multiplying: 2-digit number times a 2-digit number (standard algorithm) | In this tutorial video from Khan Academy, view an example of how to multiply a 2-digit number by another 2-digit number. Be sure to stick around for the second example! The key is understanding the value of each digit! |
| Multiplying: 3 digits times 1 digit (standard algorithm) | In this video tutorial from Khan Academy, view an example of how to solve a problem in which a 3-digit number is being multiplied by a 1-digit number using the standard algorithm. |
| Name |
Description |
| Multiplying: how to use the area model: | In this video tutorial from Khan Academy, view a demonstration of how to set-up an area model for multiplying a two-digit number by a two-digit number on graph or grid paper and then link this to the standard algorithm. |
| Multiplying: 2-digit number times a 2-digit number (area model): | In this tutorial video from Khan Academy, view an example of how to multiply a two-digit number by a two-digit number using the area model. The video makes a connection between partial products and the area model. |
| Multiplying: 2-digit number times 2-digit number (using distributive property): | In this video tutorial from Khan Academy, view an example and a description of how the distributive property can be used to multiply a two-digit number by a two-digit number. The second example uses the area model with the distributive property. |
| Multiplying: 4-digits times 1-digit (using expanded form): | In this Khan Academy video tutorial, view an example of multiplying a 4-digit number by a 1-digit number by expanding the 4-digit number and multiplying by each digit individually in an area model. This video will help to build an understanding before teaching the standard algorithm. Multiplying with a 4-digit factor is larger than some standards which limit factors to 3-digits. |
| Multiplying: 2-digit number times a 2-digit number (standard algorithm): | In this tutorial video from Khan Academy, view an example of how to multiply a 2-digit number by another 2-digit number. Be sure to stick around for the second example! The key is understanding the value of each digit! |
| Multiplying: 3 digits times 1 digit (standard algorithm): | In this video tutorial from Khan Academy, view an example of how to solve a problem in which a 3-digit number is being multiplied by a 1-digit number using the standard algorithm. |
| Name |
Description |
| Multiplying: how to use the area model: | In this video tutorial from Khan Academy, view a demonstration of how to set-up an area model for multiplying a two-digit number by a two-digit number on graph or grid paper and then link this to the standard algorithm. |
| Multiplying: 2-digit number times a 2-digit number (area model): | In this tutorial video from Khan Academy, view an example of how to multiply a two-digit number by a two-digit number using the area model. The video makes a connection between partial products and the area model. |
| Multiplying: 2-digit number times 2-digit number (using distributive property): | In this video tutorial from Khan Academy, view an example and a description of how the distributive property can be used to multiply a two-digit number by a two-digit number. The second example uses the area model with the distributive property. |
| Multiplying: 4-digits times 1-digit (using expanded form): | In this Khan Academy video tutorial, view an example of multiplying a 4-digit number by a 1-digit number by expanding the 4-digit number and multiplying by each digit individually in an area model. This video will help to build an understanding before teaching the standard algorithm. Multiplying with a 4-digit factor is larger than some standards which limit factors to 3-digits. |
| Multiplying: 2-digit number times a 2-digit number (standard algorithm): | In this tutorial video from Khan Academy, view an example of how to multiply a 2-digit number by another 2-digit number. Be sure to stick around for the second example! The key is understanding the value of each digit! |
| Multiplying: 3 digits times 1 digit (standard algorithm): | In this video tutorial from Khan Academy, view an example of how to solve a problem in which a 3-digit number is being multiplied by a 1-digit number using the standard algorithm. |
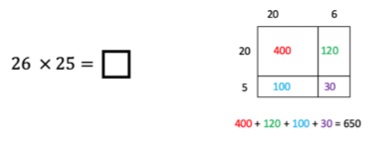

.png)