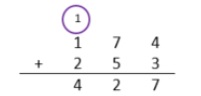
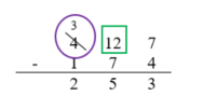
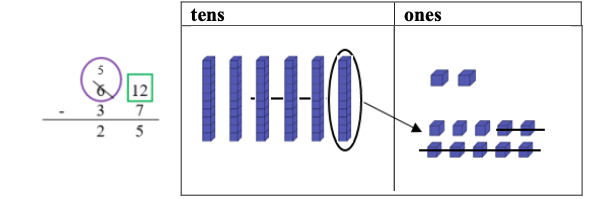
Add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers including using a standard algorithm with procedural fluency.
| Name |
Description |
| Ice Ice Maybe: An Operations Estimation Game |
This fun and interactive game helps practice estimation skills, using various operations of choice, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, using decimals, fractions, and percents.
Various levels of difficulty make this game appropriate for multiple age and ability levels.
Addition/Subtraction: The addition and subtraction of whole numbers, the addition and subtraction of decimals.
Multiplication/Division: The multiplication and addition of whole numbers.
Percentages: Identify the percentage of a whole number.
Fractions: Multiply and divide a whole number by a fraction, as well as apply properties of operations. |
| Estimator Quiz | In this activity, students are quizzed on their ability to estimate sums, products, and percentages. The student can adjust the difficulty of the problems and how close they have to be to the actual answer. This activity allows students to practice estimating addition, multiplication, or percentages of large numbers. This activity includes supplemental materials, including background information about the topics covered, a description of how to use the application, and exploration questions for use with the java applet. |
| Name |
Description |
| Food Drive | A data table is given listing class donations to a food drive. Students interpret the data and answer questions using addition and subtraction. Students discuss the importance of, volunteerism and ways that they can help their community. |
| Blowin' Around the House | In this engineering design challenge, student teams will design a house that will withstand high winds. |
| Rampin' It Up | Students will use their knowledge of properties of materials and measurement of length to determine how the properties of different surfaces affect the distance traveled by a toy car. |
| DOLO - Dinosaurs Only Live Once? | During this activity, students will create an incubator to save the last dinosaur eggs. Students will use their knowledge of energy to develop a strategy and choose which materials would be best for their dinosaur egg incubator. |
| Astounding Addition | Students will solve real-world addition problems within 1,000 using strategies and an algorithm and justify their solutions. |
| "Amazing Race-Elapsed Time" | In this lesson, which focuses specifically on the elapsed time portion of the standard, students work in small groups in a "race" to solve real world problems involving time. |
| Science Space Camp | This MEA asks the students to compare information provided on various Science Space Camps to be attended by a student during the summer. They will take into account past attendees' reviews of the camps which should create interesting student discussions. They will use knowledge of operations to determine the difference in camp costs.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. Click here to learn more about MEAs and how they can transform your classroom. |
| Let's Think in Small Units | In this lesson students will make and complete tables to express larger unit measurements in terms of a smaller unit within one system of units. They will use the chart to make comparisons and explain their reasoning. |
| Treehouse Makeover MEA | In this Model Eliciting Activity, MEA, The Shady Oak Treehouse Club is doing a makeover and needs help choosing flooring. Students will be asked to figure area, calculate cost, and add installation fees to cost. The students will then rank the flooring and choose the best one for the makeover. The data provided is: a model of the treehouse (in square yards), flooring price per square yard, and ratings for ease of cleaning, comfort, and color choices. In the twist, student will be provided with an installation fee for each flooring material and must decide if, and how, to change their procedure with the new information.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student-centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Perfect Pool Plans | In this Model Eliciting Activity, MEA, students will create a procedure for ranking pool construction companies based on the number of years in business, customer satisfaction, and available pool dimensions. In a “twist,” students will be given information about discounts available by each company. Students will evaluate their procedure for ranking and change it if necessary.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student-centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Field Day Fun | In this Model Eliciting Activity, MEA, students will choose their top choices of field day activities given the area required for event, safety concerns, clean up required, number of students that can play at a time, and peer comments about the activity. Students will need to make trade-offs in cost when the "twist" provides budget restrictions. Students will count unit squares to calculate area, multiply one-digit numbers by multiples of ten, and add multi-digit whole numbers.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem, while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought process. MEAs follow a problem-based, student-centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEA’s visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Kites for Education MEA | Kites for Education is a Modeling Eliciting Activity which presents students with an engineering challenge in which they must analyze data sets and develop a procedure for ranking different kite models. The product ranked as best by the students will hypothetically be sold to customers and the profit used to purchase school textbooks and supplies for school age children impacted by Haiti's devastating earthquake.
Model Eliciting Activities, MEAs, are open-ended, interdisciplinary problem-solving activities that are meant to reveal students’ thinking about the concepts embedded in realistic situations. MEAs resemble engineering problems and encourage students to create solutions in the form of mathematical and scientific models. Students work in teams to apply their knowledge of science and mathematics to solve an open-ended problem while considering constraints and tradeoffs. Students integrate their ELA skills into MEAs as they are asked to clearly document their thought processes. MEAs follow a problem-based, student-centered approach to learning, where students are encouraged to grapple with the problem while the teacher acts as a facilitator. To learn more about MEAs visit: https://www.cpalms.org/cpalms/mea.aspx |
| Jumping Beans: Adding with Open Number Lines | Students will use the open number line as a strategy to add within 1,000. The lesson begins with a formative assessment that evaluates students' strategies for efficiently solving addition sentences within 1,000. In order for students to have practice reinforcing the skill, students will complete the guided practice with open number lines, as well as playing the game, Jumping Beans. To conclude the lesson, students will evaluate a solution to an open number line problem. |
| Subtraction Attraction | In this lesson, students will demonstrate fluency in using a standard algorithm to complete story problems involving subtraction with regrouping using multi-digit whole numbers. |
| Rip and Regroup to Add | Students will learn how to transpose a horizontal addition equation with two-digit addends using a specialized vertical place value work mat. Students will "rip and regroup" to help understand how to regroup ten ones as one ten and move toward using a standard algorithm for addition. |
| Decoding Decomposing {Adding two 3-digit Numbers} | Students will add 3-digit numbers by decomposing them by place value. It is a useful lesson to reinforce place value concepts when adding. |
| Name |
Description |
| Addition Within 100 Strategies | Explore ways students may solve addition problems within 100 and how to support their understanding in this video.
FCR-STEM’s Count Us In! initiative is designed to support out-of-school providers and parents in fostering math success and enjoyment among K-5 children. |
| Subraction Within 100 Strategies | Explore strategies students may use to solve subtraction problems within 100 and ways to support their understanding by watching this video.
FCR-STEM’s Count Us In! initiative is designed to support out-of-school providers and parents in fostering math success and enjoyment among K-5 children. |
| Fluency vs. Automaticity | How are fluency and automaticity defined? Dr. Lawrence Gray explains fluency and automaticity in the B.E.S.T. mathematics benchmarks in this Expert Perspectives video. |
| The Role of Procedures in Fluency | What are the components to a good procedure? Dr. Lawrence Gray discusses the role of procedures in the path to fluency in this Expert Perspectives video. |
| That's Not How I Learned it: Why today's math may look different | Why do students need "a" good procedure for the arithmetic operations? Dr. Lawrence Gray explains why math may look different than in the past in this Expert Perspectives video. |
| B.E.S.T. Journey | What roles do exploration, procedural reliability, automaticity, and procedural fluency play in a student's journey through the B.E.S.T. benchmarks? Dr. Lawrence Gray explains the path through the B.E.S.T. mathematics benchmarks in this Expert Perspectives video. |
| Why Isn't Getting the "Right" Answer Good Enough? | Why is it important to look beyond whether a student gets the right answer? Dr. Lawrence Gray explores the importance of understanding why we perform certain steps or what those steps mean, and the impact this understanding can have on our ability to solve more complex problems and address them in the context of real life in this Expert Perspectives video. |
| A Standard Algorithm | Ever wonder why the benchmarks say, “a standard algorithm,” instead of, “the standard algorithm?" Dr. Lawrence Gray explores the role that standard algorithms can play in building and exhibiting procedural fluency through this Expert Perspectives video. |
| Name |
Description |
| Ice Ice Maybe: An Operations Estimation Game: |
This fun and interactive game helps practice estimation skills, using various operations of choice, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, using decimals, fractions, and percents.
Various levels of difficulty make this game appropriate for multiple age and ability levels.
Addition/Subtraction: The addition and subtraction of whole numbers, the addition and subtraction of decimals.
Multiplication/Division: The multiplication and addition of whole numbers.
Percentages: Identify the percentage of a whole number.
Fractions: Multiply and divide a whole number by a fraction, as well as apply properties of operations. |
| Estimator Quiz: | In this activity, students are quizzed on their ability to estimate sums, products, and percentages. The student can adjust the difficulty of the problems and how close they have to be to the actual answer. This activity allows students to practice estimating addition, multiplication, or percentages of large numbers. This activity includes supplemental materials, including background information about the topics covered, a description of how to use the application, and exploration questions for use with the java applet. |