General Information
Benchmark Instructional Guide
Connecting Benchmarks/Horizontal Alignment
Terms from the K-12 Glossary
- NA
Vertical Alignment
Previous Benchmarks
Next Benchmarks
Purpose and Instructional Strategies
The purpose of this benchmark is to introduce the concept of even and odd numbers by building on students' understanding of equal groups and equal addends while continuing to build their automaticity with basic facts. This work lays the foundation for understanding multiples of 2 (MTR.5.1).- Instruction includes the use of arrays to show equal groups in rows and columns.
- Instruction includes the use of manipulatives, drawings, models, or equations to show a number as even or odd.
- Instruction includes numbers no larger than 25.
- Instruction includes building the foundation for patterns in grade 3.
Common Misconceptions or Errors
- Students may think a number is odd if the doubles addition fact involves odd numbers.
Strategies to Support Tiered Instruction
- Instruction includes opportunities to draw models of double facts or use two-color counters to explore the sums produced. Focus should be on sums always being even.
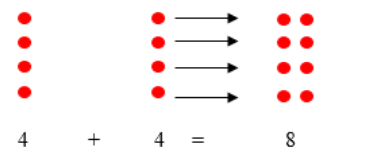
- For example, students draw a model for 4 + 4 and 9 + 9 by drawing a column of circles to represent each number. Students then pair the circle in each row to see there are no circles left without a match even when odd addends are used. Enough examples should be completed for students to see the pattern in the sums and realize the sums will always be even.
- Instruction includes opportunities to build models of numbers using two-color counters to determine if a number is even or odd.
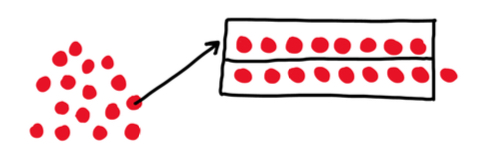
- For example, using 15 two-color counters, students pair the counters together to determine if each counter will have a partner or if one counter will be left without a partner. Students will determine if the number is even or odd by developing the understanding that an even number can be split into two equal groups.
Instructional Tasks
Instructional Task 1 (MTR.5.1)
Present students with a variety of numbers between 0 and 25. Ask students to determine if the given number is even or odd by visually representing groups and creating an expression to determine if the total number of counters is even or odd. Student discussion should center around students being able to make generalizations about odd and even numbers.
Instructional Items
Instructional Item 1
The counters below represent the number 10. Use groups and an expression to justify if the number 10 is even or odd.
Instructional Item 2
Tim says 15 is odd because there is a 5 in the ones place. Use an array to show that he is correct.*The strategies, tasks and items included in the B1G-M are examples and should not be considered comprehensive.
