| Name |
Description |
| MA.912.AR.1.1: | Identify and interpret parts of an equation or expression that represent a quantity in terms of a mathematical or real-world context, including viewing one or more of its parts as a single entity.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Parts of an expression include factors, terms, constants, coefficients and variables. Clarification 2: Within the Mathematics for Data and Financial Literacy course, problem types focus on money and business. |
|
| MA.912.AR.1.3: | Add, subtract and multiply polynomial expressions with rational number coefficients.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Instruction includes an understanding that when any of these operations are performed with polynomials the result is also a polynomial.Clarification 2: Within the Algebra 1 course, polynomial expressions are limited to 3 or fewer terms.
|
|
| MA.912.AR.1.5: | Divide polynomial expressions using long division, synthetic division or algebraic manipulation. |
| MA.912.AR.1.6: | Solve mathematical and real-world problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication or division of polynomials. |
| MA.912.AR.1.8: | Rewrite a polynomial expression as a product of polynomials over the real or complex number system.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Instruction includes factoring a sum or difference of squares and a sum or difference of cubes. |
|
| MA.912.AR.1.9: | Apply previous understanding of rational number operations to add, subtract, multiply and divide rational algebraic expressions.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Instruction includes the connection to fractions and common denominators. |
|
| MA.912.AR.1.11: | Apply the Binomial Theorem to create equivalent polynomial expressions.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Instruction includes the connection to Pascal’s Triangle and to combinations. |
|
| MA.912.AR.3.2: | Given a mathematical or real-world context, write and solve one-variable quadratic equations over the real and complex number systems.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Within this benchmark, the expectation is to solve by factoring techniques, taking square roots, the quadratic formula and completing the square. |
|
| MA.912.AR.3.3: | Given a mathematical or real-world context, write and solve one-variable quadratic inequalities over the real number system. Represent solutions algebraically or graphically. |
| MA.912.AR.3.4: | Write a quadratic function to represent the relationship between two quantities from a graph, a written description or a table of values within a mathematical or real-world context.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Within the Algebra 1 course, a graph, written description or table of values must include the vertex and two points that are equidistant from the vertex.Clarification 2: Instruction includes the use of standard form, factored form and vertex form. Clarification 3: Within the Algebra 2 course, one of the given points must be the vertex or an x-intercept.
|
Examples:
Algebra I Example: Given the table of values below from a quadratic function, write an equation of that function.
x
| -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 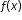
| 2 | -1 | -2 | -1 | 2 |
|
|
| MA.912.AR.3.8: | Solve and graph mathematical and real-world problems that are modeled with quadratic functions. Interpret key features and determine constraints in terms of the context.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Key features are limited to domain; range; intercepts; intervals where the function is increasing, decreasing, positive or negative; end behavior; vertex; and symmetry.Clarification 2: Instruction includes the use of standard form, factored form and vertex form. Clarification 3: Instruction includes representing the domain, range and constraints with inequality notation, interval notation or set-builder notation. Clarification 4: Within the Algebra 1 course, notations for domain, range and constraints are limited to inequality and set-builder.
|
Examples:
Algebra 1 Example: The value of a classic car produced in 1972 can be modeled by the function 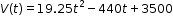 , where t is the number of years since 1972. In what year does the car’s value start to increase? , where t is the number of years since 1972. In what year does the car’s value start to increase? |
|
| MA.912.AR.3.9: | Given a mathematical or real-world context, write two-variable quadratic inequalities to represent relationships between quantities from a graph or a written description.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Instruction includes the use of standard form, factored form and vertex form where any inequality symbol can be represented. |
|
| MA.912.AR.3.10: | Given a mathematical or real-world context, graph the solution set to a two-variable quadratic inequality.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Instruction includes the use of standard form, factored form and vertex form where any inequality symbol can be represented. |
|
| MA.912.AR.4.2: | Given a mathematical or real-world context, write and solve one-variable absolute value inequalities. Represent solutions algebraically or graphically. |
| MA.912.AR.4.4: | Solve and graph mathematical and real-world problems that are modeled with absolute value functions. Interpret key features and determine constraints in terms of the context.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Key features are limited to domain; range; intercepts; intervals where the function is increasing, decreasing, positive or negative; vertex; end behavior and symmetry.Clarification 2: Instruction includes representing the domain, range and constraints with inequality notation, interval notation or set-builder notation.
|
|
| MA.912.AR.5.2: | Solve one-variable equations involving logarithms or exponential expressions. Interpret solutions as viable in terms of the context and identify any extraneous solutions. |
| MA.912.AR.5.4: | Write an exponential function to represent a relationship between two quantities from a graph, a written description or a table of values within a mathematical or real-world context. |
| MA.912.AR.5.5: | Given an expression or equation representing an exponential function, reveal the constant percent rate of change per unit interval using the properties of exponents. Interpret the constant percent rate of change in terms of a real-world context. |
| MA.912.AR.5.7: | Solve and graph mathematical and real-world problems that are modeled with exponential functions. Interpret key features and determine constraints in terms of the context.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Key features are limited to domain; range; intercepts; intervals where the function is increasing, decreasing, positive or negative; constant percent rate of change; end behavior and asymptotes. Clarification 2: Instruction includes representing the domain, range and constraints with inequality notation, interval notation or set-builder notation. Clarification 3: Instruction includes understanding that when the logarithm of the dependent variable is taken and graphed, the exponential function will be transformed into a linear function. Clarification 4: Within the Mathematics for Data and Financial Literacy course, problem types focus on money and business.
|
Examples:
The graph of the function 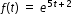 can be transformed into the straight line y=5t+2 by taking the natural logarithm of the function’s outputs. can be transformed into the straight line y=5t+2 by taking the natural logarithm of the function’s outputs. |
|
| MA.912.AR.5.8: | Given a table, equation or written description of a logarithmic function, graph that function and determine its key features.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Key features are limited to domain; range; intercepts; intervals where the function is increasing, decreasing, positive or negative; end behavior; and asymptotes.
Clarification 2: Instruction includes representing the domain and range with inequality notation, interval notation or set-builder notation.
|
|
| MA.912.AR.5.9: | Solve and graph mathematical and real-world problems that are modeled with logarithmic functions. Interpret key features and determine constraints in terms of the context.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Key features are limited to domain; range; intercepts; intervals where the function is increasing, decreasing, positive or negative; end behavior; and asymptotes.Clarification 2: Instruction includes representing the domain, range and constraints with inequality notation, interval notation or set-builder notation.
|
|
| MA.912.AR.6.1: | Given a mathematical or real-world context, when suitable factorization is possible, solve one-variable polynomial equations of degree 3 or higher over the real and complex number systems. |
| MA.912.AR.6.2: | Explain and apply the Remainder Theorem to solve mathematical and real-world problems. |
| MA.912.AR.6.5: | Sketch a rough graph of a polynomial function of degree 3 or higher using zeros, multiplicity and knowledge of end behavior. |
| MA.912.AR.7.1: | Solve one-variable radical equations. Interpret solutions as viable in terms of context and identify any extraneous solutions. |
| MA.912.AR.7.2: | Given a table, equation or written description of a square root or cube root function, graph that function and determine its key features.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Key features are limited to domain; range; intercepts; intervals where the function is increasing, decreasing, positive or negative; end behavior; and relative maximums and minimums.
Clarification 2: Instruction includes representing the domain and range with inequality notation, interval notation or set-builder notation.
|
|
| MA.912.AR.7.3: | Solve and graph mathematical and real-world problems that are modeled with square root or cube root functions. Interpret key features and determine constraints in terms of the context.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Key features are limited to domain; range; intercepts; intervals where the function is increasing, decreasing, positive or negative; end behavior; and relative maximums and minimums.Clarification 2: Instruction includes representing the domain, range and constraints with inequality notation, interval notation or set-builder notation.
|
|
| MA.912.AR.8.1: | Write and solve one-variable rational equations. Interpret solutions as viable in terms of the context and identify any extraneous solutions.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Within the Algebra 2 course, numerators and denominators are limited to linear and quadratic expressions. |
|
| MA.912.AR.8.2: | Given a table, equation or written description of a rational function, graph that function and determine its key features.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Key features are limited to domain; range; intercepts; intervals where the function is increasing, decreasing, positive or negative; end behavior; and asymptotes.Clarification 2: Instruction includes representing the domain and range with inequality notation, interval notation or set-builder notation. Clarification 3: Within the Algebra 2 course, numerators and denominators are limited to linear and quadratic expressions.
|
|
| MA.912.AR.8.3: | Solve and graph mathematical and real-world problems that are modeled with rational functions. Interpret key features and determine constraints in terms of the context.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Key features are limited to domain; range; intercepts; intervals where the function is increasing, decreasing, positive or negative; end behavior; and asymptotes.Clarification 2: Instruction includes representing the domain, range and constraints with inequality notation, interval notation or set-builder notation. Clarification 3: Instruction includes using rational functions to represent inverse proportional relationships. Clarification 4: Within the Algebra 2 course, numerators and denominators are limited to linear and quadratic expressions.
|
|
| MA.912.AR.9.2: | Given a mathematical or real-world context, solve a system consisting of a two-variable linear equation and a non-linear equation algebraically or graphically. |
| MA.912.AR.9.3: | Given a mathematical or real-world context, solve a system consisting of two-variable linear or non-linear equations algebraically or graphically.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Within the Algebra 2 course, non-linear equations are limited to quadratic equations. |
|
| MA.912.AR.9.5: | Graph the solution set of a system of two-variable inequalities.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Within the Algebra 2 course, two-variable inequalities are limited to linear and quadratic. |
|
| MA.912.AR.9.7: | Given a real-world context, represent constraints as systems of linear and non-linear equations or inequalities. Interpret solutions to problems as viable or non-viable options.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Instruction focuses on analyzing a given function that models a real-world situation and writing constraints that are represented as non-linear equations or non-linear inequalities. Clarification 2: Within the Algebra 2 course, non-linear equations and inequalities are limited to quadratic.
|
|
| MA.912.AR.9.10: | Solve and graph mathematical and real-world problems that are modeled with piecewise functions. Interpret key features and determine constraints in terms of the context.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Key features are limited to domain, range, intercepts, asymptotes and end behavior.Clarification 2: Instruction includes representing the domain, range and constraints with inequality notation, interval notation or set-builder notation.
|
Examples:
A mechanic wants to place an ad in his local newspaper. The cost, in dollars, of an ad x inches long is given by the following piecewise function. Find the cost of an ad that would be 16 inches long. 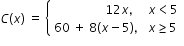
|
|
| MA.912.AR.10.1: | Given a mathematical or real-world context, write and solve problems involving arithmetic sequences.
Examples:
Tara is saving money to move out of her parent’s house. She opens the account with $250 and puts $100 into a savings account every month after that. Write the total amount of money she has in her account after each month as a sequence. In how many months will she have at least $3,000? |
|
| MA.912.AR.10.2: | Given a mathematical or real-world context, write and solve problems involving geometric sequences.
Examples:
A bacteria in a Petri dish initially covers 2 square centimeters. The bacteria grows at a rate of 2.6% every day. Determine the geometric sequence that describes the area covered by the bacteria after 0,1,2,3… days. Determine using technology, how many days it would take the bacteria to cover 10 square centimeters. |
|
| MA.912.DP.2.8: | Fit a quadratic function to bivariate numerical data that suggests a quadratic association and interpret any intercepts or the vertex of the model. Use the model to solve real-world problems in terms of the context of the data.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Problems include making a prediction or extrapolation, inside and outside the range of the data, based on the equation of the line of fit. |
|
| MA.912.DP.2.9: | Fit an exponential function to bivariate numerical data that suggests an exponential association. Use the model to solve real-world problems in terms of the context of the data.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Instruction focuses on determining whether an exponential model is appropriate by taking the logarithm of the dependent variable using spreadsheets and other technology.Clarification 2: Instruction includes determining whether the transformed scatterplot has an appropriate line of best fit, and interpreting the y-intercept and slope of the line of best fit. Clarification 3: Problems include making a prediction or extrapolation, inside and outside the range of the data, based on the equation of the line of fit.
|
|
| MA.912.DP.4.1: | Describe events as subsets of a sample space using characteristics, or categories, of the outcomes, or as unions, intersections or complements of other events. |
| MA.912.DP.4.2: | Determine if events A and B are independent by calculating the product of their probabilities. |
| MA.912.DP.4.3: | Calculate the conditional probability of two events and interpret the result in terms of its context. |
| MA.912.DP.4.4: | Interpret the independence of two events using conditional probability. |
| MA.912.DP.4.9: | Apply the addition and multiplication rules for counting to solve mathematical and real-world problems, including problems involving probability. |
| MA.912.DP.4.10: | Given a mathematical or real-world situation, calculate the appropriate permutation or combination. |
| MA.912.F.1.1: | Given an equation or graph that defines a function, determine the function type. Given an input-output table, determine a function type that could represent it.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Within the Algebra 1 course, functions represented as tables are limited to linear, quadratic and exponential.
Clarification 2: Within the Algebra 1 course, functions represented as equations or graphs are limited to vertical or horizontal translations or reflections over the x-axis of the following parent functions:
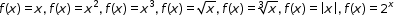 and and 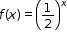 . . |
|
| MA.912.F.1.7: | Compare key features of two functions each represented algebraically, graphically, in tables or written descriptions.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Key features include domain; range; intercepts; intervals where the function is increasing, decreasing, positive or negative; end behavior and asymptotes. |
|
| MA.912.F.1.9: | Determine whether a function is even, odd or neither when represented algebraically, graphically or in a table. |
| MA.912.F.2.2: | Identify the effect on the graph of a given function of two or more transformations defined by adding a real number to the x- or y- values or multiplying the x- or y- values by a real number. |
| MA.912.F.2.3: | Given the graph or table of f(x) and the graph or table of f(x)+k,kf(x), f(kx) and f(x+k), state the type of transformation and find the value of the real number k.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Within the Algebra 1 course, functions are limited to linear, quadratic and absolute value. |
|
| MA.912.F.2.5: | Given a table, equation or graph that represents a function, create a corresponding table, equation or graph of the transformed function defined by adding a real number to the x- or y-values or multiplying the x- or y-values by a real number. |
| MA.912.F.3.2: | Given a mathematical or real-world context, combine two or more functions, limited to linear, quadratic, exponential and polynomial, using arithmetic operations. When appropriate, include domain restrictions for the new function.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Instruction includes representing domain restrictions with inequality notation, interval notation or set-builder notation.Clarification 2: Within the Mathematics for Data and Financial Literacy course, problem types focus on money and business.
|
|
| MA.912.F.3.4: | Represent the composition of two functions algebraically or in a table. Determine the domain and range of the composite function. |
| MA.912.F.3.6: | Determine whether an inverse function exists by analyzing tables, graphs and equations. |
| MA.912.F.3.7: | Represent the inverse of a function algebraically, graphically or in a table. Use composition of functions to verify that one function is the inverse of the other.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Instruction includes the understanding that a logarithmic function is the inverse of an exponential function. |
|
| MA.912.FL.3.1: | Compare simple, compound and continuously compounded interest over time.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Instruction includes taking into consideration the annual percentage rate (APR) when comparing simple and compound interest. |
|
| MA.912.FL.3.2: | Solve real-world problems involving simple, compound and continuously compounded interest.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Within the Algebra 1 course, interest is limited to simple and compound. |
Examples:
Example: Find the amount of money on deposit at the end of 5 years if you started with $500 and it was compounded quarterly at 6% interest per year. Example: Joe won $25,000 on a lottery scratch-off ticket. How many years will it take at 6% interest compounded yearly for his money to double?
|
|
| MA.912.FL.3.4: | Explain the relationship between simple interest and linear growth. Explain the relationship between compound interest and exponential growth and the relationship between continuously compounded interest and exponential growth.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Within the Algebra 1 course, exponential growth is limited to compound interest. |
|
| MA.912.NSO.1.3: | Generate equivalent algebraic expressions involving radicals or rational exponents using the properties of exponents.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Within the Algebra 2 course, radicands are limited to monomial algebraic expressions. |
|
| MA.912.NSO.1.5: | Add, subtract, multiply and divide algebraic expressions involving radicals.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Within the Algebra 2 course, radicands are limited to monomial algebraic expressions. |
|
| MA.912.NSO.1.6: | Given a numerical logarithmic expression, evaluate and generate equivalent numerical expressions using the properties of logarithms or exponents.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Within the Mathematics for Data and Financial Literacy Honors course, problem types focus on money and business. |
|
| MA.912.NSO.1.7: | Given an algebraic logarithmic expression, generate an equivalent algebraic expression using the properties of logarithms or exponents.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Within the Mathematics for Data and Financial Literacy Honors course, problem types focus on money and business. |
|
| MA.912.NSO.2.1: | Extend previous understanding of the real number system to include the complex number system. Add, subtract, multiply and divide complex numbers. |
| MA.912.NSO.4.1: | Given a mathematical or real-world context, represent and manipulate data using matrices. |
| MA.912.NSO.4.2: | Given a mathematical or real-world context, represent and solve a system of two- or three-variable linear equations using matrices. |
| MA.912.NSO.4.3: | Solve mathematical and real-world problems involving addition, subtraction and multiplication of matrices.Clarifications:
Clarification 1: Instruction includes identifying and using the additive and multiplicative identities for matrices. |
|
| MA.912.NSO.4.4: | Solve mathematical and real-world problems using the inverse and determinant of matrices. |
| MA.K12.MTR.1.1: | Actively participate in effortful learning both individually and collectively. Mathematicians who participate in effortful learning both individually and with others:
- Analyze the problem in a way that makes sense given the task.
- Ask questions that will help with solving the task.
- Build perseverance by modifying methods as needed while solving a challenging task.
- Stay engaged and maintain a positive mindset when working to solve tasks.
- Help and support each other when attempting a new method or approach.
Clarifications:
Teachers who encourage students to participate actively in effortful learning both individually and with others:
- Cultivate a community of growth mindset learners.
- Foster perseverance in students by choosing tasks that are challenging.
- Develop students’ ability to analyze and problem solve.
- Recognize students’ effort when solving challenging problems.
|
|
| MA.K12.MTR.2.1: | Demonstrate understanding by representing problems in multiple ways. Mathematicians who demonstrate understanding by representing problems in multiple ways: - Build understanding through modeling and using manipulatives.
- Represent solutions to problems in multiple ways using objects, drawings, tables, graphs and equations.
- Progress from modeling problems with objects and drawings to using algorithms and equations.
- Express connections between concepts and representations.
- Choose a representation based on the given context or purpose.
Clarifications:
Teachers who encourage students to demonstrate understanding by representing problems in multiple ways: - Help students make connections between concepts and representations.
- Provide opportunities for students to use manipulatives when investigating concepts.
- Guide students from concrete to pictorial to abstract representations as understanding progresses.
- Show students that various representations can have different purposes and can be useful in different situations.
|
|
| MA.K12.MTR.3.1: | Complete tasks with mathematical fluency. Mathematicians who complete tasks with mathematical fluency: - Select efficient and appropriate methods for solving problems within the given context.
- Maintain flexibility and accuracy while performing procedures and mental calculations.
- Complete tasks accurately and with confidence.
- Adapt procedures to apply them to a new context.
- Use feedback to improve efficiency when performing calculations.
Clarifications:
Teachers who encourage students to complete tasks with mathematical fluency:- Provide students with the flexibility to solve problems by selecting a procedure that allows them to solve efficiently and accurately.
- Offer multiple opportunities for students to practice efficient and generalizable methods.
- Provide opportunities for students to reflect on the method they used and determine if a more efficient method could have been used.
|
|
| MA.K12.MTR.4.1: | Engage in discussions that reflect on the mathematical thinking of self and others. Mathematicians who engage in discussions that reflect on the mathematical thinking of self and others: - Communicate mathematical ideas, vocabulary and methods effectively.
- Analyze the mathematical thinking of others.
- Compare the efficiency of a method to those expressed by others.
- Recognize errors and suggest how to correctly solve the task.
- Justify results by explaining methods and processes.
- Construct possible arguments based on evidence.
Clarifications:
Teachers who encourage students to engage in discussions that reflect on the mathematical thinking of self and others:- Establish a culture in which students ask questions of the teacher and their peers, and error is an opportunity for learning.
- Create opportunities for students to discuss their thinking with peers.
- Select, sequence and present student work to advance and deepen understanding of correct and increasingly efficient methods.
- Develop students’ ability to justify methods and compare their responses to the responses of their peers.
|
|
| MA.K12.MTR.5.1: | Use patterns and structure to help understand and connect mathematical concepts. Mathematicians who use patterns and structure to help understand and connect mathematical concepts: - Focus on relevant details within a problem.
- Create plans and procedures to logically order events, steps or ideas to solve problems.
- Decompose a complex problem into manageable parts.
- Relate previously learned concepts to new concepts.
- Look for similarities among problems.
- Connect solutions of problems to more complicated large-scale situations.
Clarifications:
Teachers who encourage students to use patterns and structure to help understand and connect mathematical concepts:- Help students recognize the patterns in the world around them and connect these patterns to mathematical concepts.
- Support students to develop generalizations based on the similarities found among problems.
- Provide opportunities for students to create plans and procedures to solve problems.
- Develop students’ ability to construct relationships between their current understanding and more sophisticated ways of thinking.
|
|
| MA.K12.MTR.6.1: | Assess the reasonableness of solutions. Mathematicians who assess the reasonableness of solutions: - Estimate to discover possible solutions.
- Use benchmark quantities to determine if a solution makes sense.
- Check calculations when solving problems.
- Verify possible solutions by explaining the methods used.
- Evaluate results based on the given context.
Clarifications:
Teachers who encourage students to assess the reasonableness of solutions:- Have students estimate or predict solutions prior to solving.
- Prompt students to continually ask, “Does this solution make sense? How do you know?”
- Reinforce that students check their work as they progress within and after a task.
- Strengthen students’ ability to verify solutions through justifications.
|
|
| MA.K12.MTR.7.1: | Apply mathematics to real-world contexts. Mathematicians who apply mathematics to real-world contexts: - Connect mathematical concepts to everyday experiences.
- Use models and methods to understand, represent and solve problems.
- Perform investigations to gather data or determine if a method is appropriate.
• Redesign models and methods to improve accuracy or efficiency.
Clarifications:
Teachers who encourage students to apply mathematics to real-world contexts:- Provide opportunities for students to create models, both concrete and abstract, and perform investigations.
- Challenge students to question the accuracy of their models and methods.
- Support students as they validate conclusions by comparing them to the given situation.
- Indicate how various concepts can be applied to other disciplines.
|
|
| ELA.K12.EE.1.1: | Cite evidence to explain and justify reasoning.Clarifications:
K-1 Students include textual evidence in their oral communication with guidance and support from adults. The evidence can consist of details from the text without naming the text. During 1st grade, students learn how to incorporate the evidence in their writing.2-3 Students include relevant textual evidence in their written and oral communication. Students should name the text when they refer to it. In 3rd grade, students should use a combination of direct and indirect citations. 4-5 Students continue with previous skills and reference comments made by speakers and peers. Students cite texts that they’ve directly quoted, paraphrased, or used for information. When writing, students will use the form of citation dictated by the instructor or the style guide referenced by the instructor. 6-8 Students continue with previous skills and use a style guide to create a proper citation. 9-12 Students continue with previous skills and should be aware of existing style guides and the ways in which they differ.
|
|
| ELA.K12.EE.2.1: | Read and comprehend grade-level complex texts proficiently.Clarifications:
See Text Complexity for grade-level complexity bands and a text complexity rubric. |
|
| ELA.K12.EE.3.1: | Make inferences to support comprehension.Clarifications:
Students will make inferences before the words infer or inference are introduced. Kindergarten students will answer questions like “Why is the girl smiling?” or make predictions about what will happen based on the title page.
Students will use the terms and apply them in 2nd grade and beyond. |
|
| ELA.K12.EE.4.1: | Use appropriate collaborative techniques and active listening skills when engaging in discussions in a variety of situations.Clarifications:
In kindergarten, students learn to listen to one another respectfully.In grades 1-2, students build upon these skills by justifying what they are thinking. For example: “I think ________ because _______.” The collaborative conversations are becoming academic conversations. In grades 3-12, students engage in academic conversations discussing claims and justifying their reasoning, refining and applying skills. Students build on ideas, propel the conversation, and support claims and counterclaims with evidence.
|
|
| ELA.K12.EE.5.1: | Use the accepted rules governing a specific format to create quality work.Clarifications:
Students will incorporate skills learned into work products to produce quality work. For students to incorporate these skills appropriately, they must receive instruction. A 3rd grade student creating a poster board display must have instruction in how to effectively present information to do quality work. |
|
| ELA.K12.EE.6.1: | Use appropriate voice and tone when speaking or writing.Clarifications:
In kindergarten and 1st grade, students learn the difference between formal and informal language. For example, the way we talk to our friends differs from the way we speak to adults. In 2nd grade and beyond, students practice appropriate social and academic language to discuss texts. |
|
| ELD.K12.ELL.MA.1: | English language learners communicate information, ideas and concepts necessary for academic success in the content area of Mathematics. |

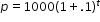 to make a prediction about the camel population in Australia. He identifies the growth factor as (1+.1), or 1.1, and states that the camel population will grow at an annual rate of 10% per year.
to make a prediction about the camel population in Australia. He identifies the growth factor as (1+.1), or 1.1, and states that the camel population will grow at an annual rate of 10% per year.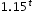 can be rewritten as
can be rewritten as 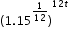 which is approximately equivalent to
which is approximately equivalent to 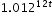 . This latter expression reveals the approximate equivalent monthly interest rate of 1.2% if the annual rate is 15%.
. This latter expression reveals the approximate equivalent monthly interest rate of 1.2% if the annual rate is 15%.
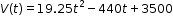 , where t is the number of years since 1972. In what year does the car’s value start to increase?
, where t is the number of years since 1972. In what year does the car’s value start to increase?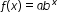 , where b is a whole number greater than 1 or a unit fraction, or
, where b is a whole number greater than 1 or a unit fraction, or 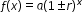 , where
, where 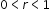 .
.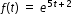 can be transformed into the straight line y=5t+2 by taking the natural logarithm of the function’s outputs.
can be transformed into the straight line y=5t+2 by taking the natural logarithm of the function’s outputs.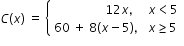
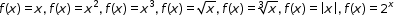 and
and 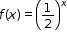 .
.