Clarifications:
Essential Understandings
Concrete:
- When given a number (correlation coefficient “r”) between 1 and -1, show by sorting cards on a number line template (with the words strong written under 1 and -1) if the correlation coefficient is closer to 1 (-1) the data has a strong correlation to the graph and x and y.
- Match descriptors of a correlation coefficient with its numeric “r” value (e.g., weak = 0.1, strong = 0.9).
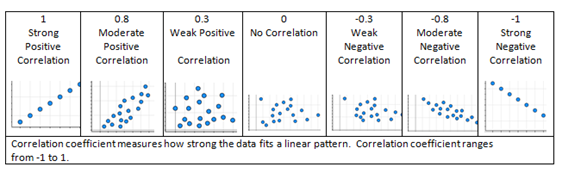
- Understand that “r” represents the correlation coefficient.
- Understand that the closer “r” is to 1 (-1) the stronger the data fits the relationship of x and y.
- Understand that the closer “r” is to 0 the weaker the data fits the relationship of x and y.
- Describe a correlation coefficient using appropriate vocabulary (e.g., positive correlation, negative correlation, no correlation or perfect [exactly 1 or -1] correlation).
- Understand the following concepts and vocabulary: correlation coefficient, linear relationship, positive correlation, negative correlation, no correlation and perfect correlation.
| Number: MAFS.912.S-ID.3.AP.8b | Category: Access Points |
| Date Adopted or Revised: 07/14 |
Cluster:
Interpret linear models. (Algebra 1 - Major Cluster) : Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters. |
