Clarifications:
Essential Understandings
Concrete:
- Use a tool to determine whether the quadratic function crosses the x-axis. Click Here
- Use a graphing tool or graphing software to find the roots (where the function intersects the x-axis) of a function.
- Use manipulatives (i.e. algebra tiles) to simplify or to write equivalent forms of quadratic functions.
- Use algebra tiles or manipulatives to complete the square.
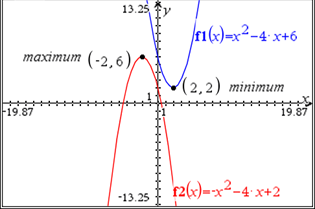
Youtube: Click Here - Use the graph of the quadratic equation to identify the vertex of the function.
- Identify the maximum or minimum of the graph of the quadratic equation.
- Understand the following concepts and vocabulary: root, factor, quadratic, integer, real number, quadratic equation, quadratic formula, square root, solution, terms, coefficient, intercept, intersect, zero, completing the square, vertex form, maximum, minimum, vertex, trinomial.
- Use steps or a template to complete the square.
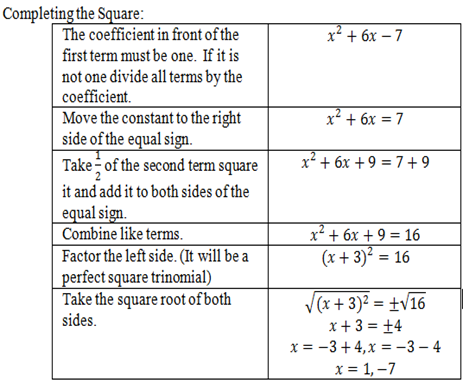
- Understand quadratic equations can be rewritten in vertex form
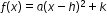 .
. - Understand that the vertex of a quadratic function is represented by (h, k). The vertex of a quadratic function is the maximum/minimum coordinate of the function. If the function opens up it is a minimum, if the function opens down it is a maximum.
For example: y=3(x+2)2-4 (Vertex form)
Vertex (h, k) = (-2, 4)
The vertex will be moved 2 units to the left and 4 units up from (0,0), the vertex of the parent function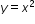 .
. - Teacher tool: Click Here
- MathBitsNotebook: Click Here
| Number: MAFS.912.A-SSE.2.AP.3d | Category: Access Points |
| Date Adopted or Revised: 07/14 |
Cluster:
Write expressions in equivalent forms to solve problems. (Algebra 1 - Supporting Cluster) (Algebra 2 - Major Cluster) : Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters. |

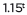 can be rewritten as
can be rewritten as 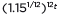 ≈
≈ 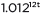 to reveal the approximate equivalent monthly interest rate if the annual rate is 15%.
to reveal the approximate equivalent monthly interest rate if the annual rate is 15%.