Clarifications:
Essential Understandings
Concrete:
- Use manipulatives (pattern blocks, two-way counters) to represent the problem.
- Use a tool (such as a mat, table or graphic organizer) to separate the expression into parts.
- Use algebra tiles to represent the expression.
- Create a model with objects to show the distributive property, combining like terms and other operations with polynomials. Click Here
- Understand the following related vocabulary and symbols: add (+), subtract (-), multiply (x), divide (÷), equal (=), base number, exponent, integer.
- Understand commutative, associative, identity, and distributive properties.
- Add, subtract, multiply, and divide variables.
- Understand the difference between coefficients and exponents.
- Combine coefficients.
- Combine exponents (rules of exponents).
- Select the correct expanded form of what an exponent represents:
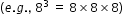 .
. - Identify the number of times the base number will be multiplied based on the exponent.
- Understand that a negative exponent will result in a fraction with a numerator of 1
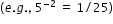 .
. - Simplify expression into expanded form:
(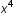 )(
)(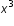 )=(xxxx)(xxx).
)=(xxxx)(xxx). - Simplify expression into the simplest form:
(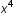 )(
)(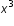 )=(xxxx)(xxx)=(xxxxxxx)=
)=(xxxx)(xxx)=(xxxxxxx)= 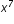 .
. - Understand the following concepts, symbols, and vocabulary for: expression, exponent, raising to a power.
- Use virtual manipulatives to represent the problem.
| Number: MAFS.912.A-SSE.1.AP.2c | Category: Access Points |
| Date Adopted or Revised: 07/14 |
Cluster:
Interpret the structure of expressions. (Algebra 1 - Major Cluster) (Algebra 2 - Major Cluster) : Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters. |
