Clarifications:
Essential Understandings
Concrete:
- Use manipulatives to represent addends in two related addition equations to show that changing the order of the addends does not change the sum.
- e.g.
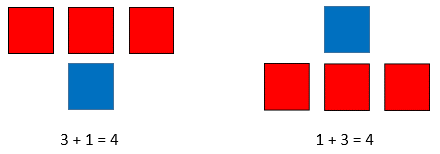
- Model two related addition equations (e.g., 1 + 5 = 6 and 5 + 1 = 6) by coloring squares on grid paper to represent each addend with a different color to show that changing the order of the addends does not change the sum.
- Identify pairs of equations that demonstrate the commutative property (e.g., match 2 + 6 = 8 with 6 + 2 = 8).
- Understand the following concepts, symbols, and vocabulary: addition, plus, equal, addends, sum, order.
| Number: MAFS.1.OA.2.AP.3a | Category: Access Points |
|
Cluster:
Understand and apply properties of operations and the relationship between addition and subtraction. (Major Cluster) : Clusters should not be sorted from Major to Supporting and then taught in that order. To do so would strip the coherence of the mathematical ideas and miss the opportunity to enhance the major work of the grade with the supporting clusters. |
